Influence of microgravity-induced intervertebral disc degeneration of rats on expression levels of p53/p16 and proinflammatory factors
- PMID: 30680015
- PMCID: PMC6327631
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.7085
Influence of microgravity-induced intervertebral disc degeneration of rats on expression levels of p53/p16 and proinflammatory factors
Abstract
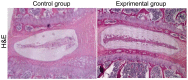
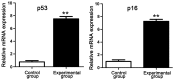
Association of expression levels of tumor suppressor proteins p53 and p16 and inflammatory factors in simulated weightlessness with the degree of lumbar disc degeneration of rats was investigated. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination was performed for rats in control group and experimental group, and the intervertebral disc of rats in both groups was detected and analyzed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) histopathological staining. The mRNA expression levels of proinflammatory factors, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were detected, and p53 and p16 mRNA and protein expression levels were detected. MRI results showed significant intervertebral disc injury in experimental group. Results of H&E staining revealed that the intervertebral disc injury in experimental group was more serious with obvious signs of degeneration than that in control group. The mRNA expression levels of inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) in rats in experimental group were significantly increased compared with those in control group, indicating that the degree of lumbar disc degeneration of rats in simulated weightlessness is closely related to the inflammatory factors. RT-PCR and western blotting proved that both p53 and p16 mRNA and protein expression levels in experimental group were obviously increased. Results of t-test manifested that there were statistically significant differences in p53 and p16 expression levels between control group and experimental group (P<0.01). The abnormal expression levels of p53 and p16 genes have close association with the degree of lumbar disc degeneration of rats in simulated weightlessness, and the lumbar disc degeneration is also closely related to the increased expression levels of inflammatory factors.
Keywords: inflammatory factors; lumbar disc degeneration; p16; p53; simulated weightlessness.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effect of curcumin on NF-κB expression in rat with lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Apr;19(7):1305-14. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25912594
-
Expression of adiponectin receptors in human and rat intervertebral disc cells and changes in receptor expression during disc degeneration using a rat tail temporary static compression model.J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 Nov 22;11(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13018-016-0481-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27876065 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of HSPA8 in Nucleus Pulposus of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc and Its Effect on Degree of Degeneration.Adv Ther. 2020 Jan;37(1):390-401. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01136-9. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 31755037
-
[Relationship between inflammatory cytokines of IL-1β and TNF-α and intervertebral disc degeneration].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2017 Sep 25;30(9):866-871. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2017.09.017. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2017. PMID: 29455492 Review. Chinese.
-
Disc in flames: Roles of TNF-α and IL-1β in intervertebral disc degeneration.Eur Cell Mater. 2015 Sep 21;30:104-16; discussion 116-7. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v030a08. Eur Cell Mater. 2015. PMID: 26388614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging role and therapeutic implications of p53 in intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 1;9(1):433. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01730-5. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38040675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Validation of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) as an Effective Countermeasure Against Inflammatory-Mediated Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.JOR Spine. 2025 May 19;8(2):e70077. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70077. eCollection 2025 Jun. JOR Spine. 2025. PMID: 40391205 Free PMC article.
-
Aucubin Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Repressing NF-κB-NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Endplate Chondrocytes.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 6;16:5899-5913. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S439981. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38084106 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the NF‑κB/p53 signaling pathway on intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus degeneration.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Sep;22(3):1821-1830. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11288. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32705171 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1-induced autophagy promotes extracellular matrix degradation leading to intervertebral disc degeneration.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 Sep 1;13(9):2240-2248. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33042328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vico L, Novikov VE, Very JM, Chappard D, Alexandre C. Effects of a 40 day tail-suspension on rat weight-bearing bones. Physiologist. 1990;33(Suppl 1):S96–S97. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
