The Genetics of Pneumothorax
- PMID: 30681372
- PMCID: PMC6543724
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201807-1212CI
The Genetics of Pneumothorax
Abstract
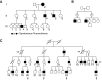
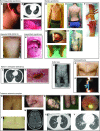
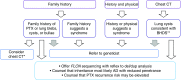
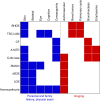
A genetic influence on spontaneous pneumothoraces-those occurring without a traumatic or iatrogenic cause-is supported by several lines of evidence: 1) pneumothorax can cluster in families (i.e., familial spontaneous pneumothorax), 2) mutations in the FLCN gene have been found in both familial and sporadic cases, and 3) pneumothorax is a known complication of several genetic syndromes. Herein, we review known genetic contributions to both sporadic and familial pneumothorax. We summarize the pneumothorax-associated genetic syndromes, including Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, Marfan syndrome, vascular (type IV) Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, tuberous sclerosis complex/lymphangioleiomyomatosis, Loeys-Dietz syndrome, cystic fibrosis, homocystinuria, and cutis laxa, among others. At times, pneumothorax is their herald manifestation. These syndromes have serious potential extrapulmonary complications (e.g., malignant renal tumors in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome), and surveillance and/or treatment is available for most disorders; thus, establishing a diagnosis is critical. To facilitate this, we provide an algorithm to guide the clinician in discerning which cases of spontaneous pneumothorax may have a genetic or familial contribution, which cases warrant genetic testing, and which cases should prompt an evaluation by a geneticist.
Keywords: gene; Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome; familial spontaneous pneumothorax; genetics; pneumothorax.
Figures
References
-
- Bense L, Lewander R, Eklund G, Hedenstierna G, Wiman LG. Nonsmoking, non-alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency-induced emphysema in nonsmokers with healed spontaneous pneumothorax, identified by computed tomography of the lungs. Chest. 1993;103:433–438. - PubMed
-
- Withers JN, Fishback ME, Kiehl PV, Hannon JL. Spontaneous pneumothorax: suggested etiology and comparison of treatment methods. Am J Surg. 1964;108:772–776. - PubMed
-
- Bense L, Eklund G, Wiman LG. Smoking and the increased risk of contracting spontaneous pneumothorax. Chest. 1987;92:1009–1012. - PubMed
-
- Abolnik IZ, Lossos IS, Zlotogora J, Brauer R. On the inheritance of primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Am J Med Genet. 1991;40:155–158. - PubMed
-
- Ren HZ, Zhu CC, Yang C, Chen SL, Xie J, Hou YY, et al. Mutation analysis of the FLCN gene in Chinese patients with sporadic and familial isolated primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Clin Genet. 2008;74:178–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

