Requirements for RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex formation in vivo
- PMID: 30681409
- PMCID: PMC6366898
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.43654
Requirements for RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex formation in vivo
Abstract
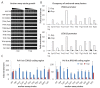
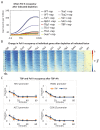
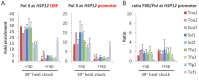
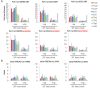
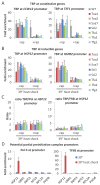
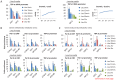
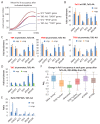
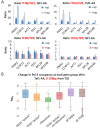
Transcription by RNA polymerase II requires assembly of a preinitiation complex (PIC) composed of general transcription factors (GTFs) bound at the promoter. In vitro, some GTFs are essential for transcription, whereas others are not required under certain conditions. PICs are stable in the absence of nucleotide triphosphates, and subsets of GTFs can form partial PICs. By depleting individual GTFs in yeast cells, we show that all GTFs are essential for TBP binding and transcription, suggesting that partial PICs do not exist at appreciable levels in vivo. Depletion of FACT, a histone chaperone that travels with elongating Pol II, strongly reduces PIC formation and transcription. In contrast, TBP-associated factors (TAFs) contribute to transcription of most genes, but TAF-independent transcription occurs at substantial levels, preferentially at promoters containing TATA elements. PICs are absent in cells deprived of uracil, and presumably UTP, suggesting that transcriptionally inactive PICs are removed from promoters in vivo.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; S. cerevisiae; TATA-binding protein; TBP-associated factors (TAFs); chromosomes; gene expression; general transcription factors; genetics; genomics; preinitiation complex; transcription.
© 2019, Petrenko et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NP, YJ, LD, KW No competing interests declared, KS Senior editor, eLife
Figures




References
-
- Brauer MJ, Huttenhower C, Airoldi EM, Rosenstein R, Matese JC, Gresham D, Boer VM, Troyanskaya OG, Botstein D. Coordination of growth rate, cell cycle, stress response, and metabolic activity in yeast. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2008;19:352–367. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-08-0779. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

