Whole body periodic acceleration improves survival and microvascular leak in a murine endotoxin model
- PMID: 30682019
- PMCID: PMC6347233
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208681
Whole body periodic acceleration improves survival and microvascular leak in a murine endotoxin model
Abstract
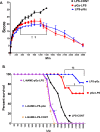
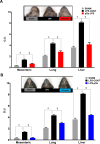
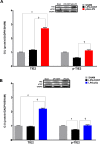
Sepsis is a life threatening condition which produces multi-organ dysfunction with profound circulatory and cellular derangements. Administration of E.Coli endotoxin (LPS) produces systemic inflammatory effects of sepsis including disruption of endothelial barrier, and if severe enough death. Whole body periodic acceleration (pGz) is the headward-footward motion of the body. pGz has been shown to induce pulsatile shear stress to the endothelium, thereby releasing vascular and cardio protective mediators. The purpose of this study was to determine whether or not pGz performed as a pre-treatment or post-treatment strategy improves survival in a lethal murine endotoxin model.This study was designed as a prospective randomized controlled study in mice. pGz was performed in mice as pre-treatment (pGz-LPS, 3 days prior to LPS), post-treatment (LPS- pGz, 30 min after LPS) strategies or Control (LPS-CONT), in a lethal murine model of endotoxemia. Endotoxemia was induced with intraperitoneal injection of E.Coli LPS (40mg/kg). In a separate group of mice, a nonspecific nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (L-NAME) was provided in their drinking water and pGz-LPS and LPS-pGz performed to determine the effect of nitric oxide (NO) inhibition on survival. In another subset of mice, micro vascular leakage was determined. Behavioral scoring around the clock was performed in all mice at 30 min intervals after LPS administration, until 48 hrs. survival or death. LPS induced 100% mortality in LPS-CONT animals by 30 hrs. In contrast, survival to 48 hrs. occurred in 60% of pGz-LPS and 80% of LPS-pGz. L-NAME abolished the survival effects of pGz. Microvascular leakage was markedly reduced in both pre and post pGz treated animals and was associated with increased tyrosine kinase endothelial-enriched tunica interna endothelial cell kinase 2 (TIE2) receptor and its phosphorylation (p-TIE2). In a murine model of lethal endotoxemia, pGz performed as a pre or post treatment strategy significantly improved survival, and markedly reduced microvascular leakage. The effect was modulated, in part, by NO since a non-selective inhibitor of NO abolished the pGz survival effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The following authors AU, JRL have declared that no competing interests exist. JAA owns minimal number of stocks in Noninvasive Monitoring Systems (NIMS), a company which manufactures a platform similar to the one described in this study. MAS is president of Sackner Wellness Products, a company which manufactures a wellness device called Gentle Jogger (a passive jogging device (JD)) referenced in the manuscript. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole body periodic acceleration (pGz) improves endotoxin induced cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction and attenuates the inflammatory response in mice.Heliyon. 2021 Mar 12;7(3):e06444. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06444. eCollection 2021 Mar. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33748496 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Pulsatile Shear Stress Modifies Endothelial Activation; A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 28;10(12):3050. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123050. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased constitutive nitric oxide production by whole body periodic acceleration ameliorates alterations in cardiomyocytes associated with utrophin/dystrophin deficiency.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Jul;108:149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 13. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28623080
-
Whole body periodic acceleration (pGz) preserves heart rate variability after cardiac arrest.Resuscitation. 2016 Feb;99:20-5. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2015.11.018. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Resuscitation. 2016. PMID: 26690649
-
Dose-Dependent Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on the Endothelium-Sepsis versus Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Cellular Senescence.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;13(4):443. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040443. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671891 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole body periodic acceleration (pGz) improves endotoxin induced cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction and attenuates the inflammatory response in mice.Heliyon. 2021 Mar 12;7(3):e06444. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06444. eCollection 2021 Mar. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33748496 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Pulsatile Shear Stress Modifies Endothelial Activation; A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 28;10(12):3050. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123050. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial pulsatile shear stress is a backstop for COVID-19.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020 Dec 11;4(4):379-387. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20200260. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33200786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Nonrandomized Trial of the Effects of Passive Simulated Jogging on Short-Term Heart Rate Variability in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects.J Diabetes Res. 2023 Apr 11;2023:4454396. doi: 10.1155/2023/4454396. eCollection 2023. J Diabetes Res. 2023. PMID: 37082380 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Enhancing Muscle Intracellular Ca2+ Homeostasis and Glucose Uptake: Passive Pulsatile Shear Stress Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 22;11(10):2596. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102596. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37892970 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

