Protective effects of hypercapnic acidosis on Ischemia-reperfusion-induced retinal injury
- PMID: 30682118
- PMCID: PMC6347245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211185
Protective effects of hypercapnic acidosis on Ischemia-reperfusion-induced retinal injury
Abstract
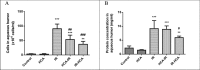
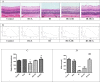
Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury is associated with numerous retinal diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, acute glaucoma, and other vascular retinopathies. Hypercapnic acidosis (HCA) has a protective effect on lung, myocardial, and central nervous system ischemic injury models. However, no study has evaluated its protective effects in an experimental retinal I/R injury model. In this study, retinal I/R injury was induced in Sprague Dawley rats by elevating the intraocular pressure to 110 mmHg for 60 minutes. HCA was induced before and after the injury. After 24 hours, the terminal dUTP nick end labeling assay was performed. Moreover, the ratios of cleaved caspase-3/total caspase-3, phosphorylated IκB/IκB, and phosphorylated p38 were measured through Western blotting. After 7 days, the rats' aqueous humor was analyzed. In addition, electroretinography and retinal thickness measurement were performed in the rats. Moreover, the retinal neural cell line RGC-5 was exposed to 500 μM H2O2 for 24 hours to induce a sustained oxidative stress in vitro. The effects of HCA were evaluated by comparing oxidative stress, MAPK signals, NF-κB signals, survival rates, and apoptosis rates in the RGC-5 cells before and after H2O2 exposure. We further investigated whether the potent I/R-protective heat shock protein (HSP) 32 contribute to protective effects of HCA. Our results indicated that HCA has protective effects against retinal I/R injury both in vivo and in vitro, at multiple levels, including antiapoptotic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and functional retinal cell protection. Further research clarifying the role of HCA in retinal I/R injury prevention and treatment is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chitosan oligosaccharides prevented retinal ischemia and reperfusion injury via reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in rats.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Jan;130:38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.12.001. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25479043
-
Protective effect of hypercapnic acidosis in ischemia-reperfusion lung injury is attributable to upregulation of heme oxygenase-1.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 10;8(9):e74742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074742. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040332 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of glucosamine on oxidative-stress and ischemia/reperfusion-induced retinal injury.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Feb 5;56(3):1506-16. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-15726. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25655796
-
Bench-to-bedside review: hypercapnic acidosis in lung injury--from 'permissive' to 'therapeutic'.Crit Care. 2010;14(6):237. doi: 10.1186/cc9238. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 21067531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypercapnia and acidosis in sepsis: a double-edged sword?Anesthesiology. 2010 Feb;112(2):462-72. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181ca361f. Anesthesiology. 2010. PMID: 20068449 Review.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic importance of acid-base balance.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;183:114278. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114278. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33039418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon dioxide and MAPK signalling: towards therapy for inflammation.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Oct 10;21(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01306-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37817178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homer1a reduces inflammatory response after retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Jul 1;19(7):1608-1617. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.386490. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38051906 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Organic Framework (COF): A Drug and Carrier to Attenuate Retinal Ganglion Cells Death in an Acute Glaucoma Mouse Model.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Aug 10;14(16):3265. doi: 10.3390/polym14163265. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015521 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Imaging of Ischemia/Reperfusion-mediated Aminopeptidase N Expression in Surgical Rat Model Using 68Ga-NOTA-c(NGR).In Vivo. 2022 Mar-Apr;36(2):657-666. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12750. In Vivo. 2022. PMID: 35241519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson DR, Davis EB. Sensitivities of ocular tissues to acute pressure-induced ischemia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975;93: 267–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

