Histomorphometric analysis of the human internal thoracic artery and relationship with cardiovascular risk factors
- PMID: 30682154
- PMCID: PMC6347214
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211421
Histomorphometric analysis of the human internal thoracic artery and relationship with cardiovascular risk factors
Abstract
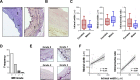
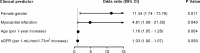
In this study, we aimed at performing a histomorphometric analysis of human left internal thoracic artery (ITA) samples as well as at correlating the histomorphometric findings with the clinical profile, including risk factors and medication. Distal segments of ITA were obtained from 54 patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Histological observation was performed in paraffin-embedded transverse sections of ITA through four staining protocols: hematoxylin-eosin, van Gieson, Masson's trichrome and von Kossa. Morphometric analysis included the intimal width (IW), medial width (MW) and intima/media ratio (IMR). No overt atherosclerotic lesions were observed. Mild calcifications were observed across the vascular wall layers in almost all samples. Multivariable linear regression analysis showed associations between IW and IMR and the following clinical variables: age, gender, kidney function expressed as eGFR and myocardial infarction history. Age (odds ratio = 1.16, P = 0.004), female gender (odds ratio = 11.34, P = 0.011), eGFR (odds ratio = 1.03, P = 0.059) and myocardial infarction history (odds ratio = 4.81, P = 0.040) were identified as the main clinical predictors for intimal hyperplasia. Preatherosclerotic lesions in ITA samples from patients undergoing coronary revascularization were associated not only with classical cardiovascular risk factors such as age and gender, but also with other clinical variables, namely kidney function and myocardial infarction history.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histomorphometric and sympathetic innervation of the human internal thoracic artery.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011;66(1):131-6. doi: 10.1590/s1807-59322011000100023. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011. PMID: 21437449 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative histopathology of radial artery versus internal thoracic artery and risk factors for development of intimal hyperplasia and atherosclerosis.Circulation. 1999 Nov 9;100(19 Suppl):II139-44. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.100.suppl_2.ii-139. Circulation. 1999. PMID: 10567293
-
Histomorphologic superiority of internal thoracic arteries over right gastroepiploic arteries for coronary bypass.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Jun;151(6):1704-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.02.018. Epub 2016 Feb 16. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 26971376
-
Reusing the patent internal mammary artery as a conduit in redo coronary artery bypass surgery.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016 Mar;22(3):346-50. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivv338. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 26669852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrastructural and histomorphologic properties of the internal thoracic artery: implications for coronary revascularization.Coron Artery Dis. 2017 Sep;28(6):518-527. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000527. Coron Artery Dis. 2017. PMID: 28678142 Review.
Cited by
-
The incidence rate and histological characteristics of intimal hyperplasia in elastase-induced experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice.Animal Model Exp Med. 2024 Jun;7(3):388-395. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12362. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Animal Model Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38017222 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Angiogenesis and Arteriogenesis in Myocardial Infarction and Coronary Revascularization.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022 Oct;15(5):1024-1048. doi: 10.1007/s12265-022-10241-0. Epub 2022 Mar 31. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35357670 Review.
References
-
- O'Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Savage PJ, Borhani NO, Kittner SJ, et al. Thickening of the carotid wall. A marker for atherosclerosis in the elderly? Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. Stroke. 1996;27(2):224–31. Epub 1996/02/01. . - PubMed
-
- O'Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr. Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(1):14–22. Epub 1999/01/08. 10.1056/NEJM199901073400103 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chambless LE, Folsom AR, Clegg LX, Sharrett AR, Shahar E, Nieto FJ, et al. Carotid wall thickness is predictive of incident clinical stroke: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151(5):478–87. Epub 2000/03/09. . - PubMed
-
- Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Grobbee DE. Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction: the Rotterdam Study. Circulation. 1997;96(5):1432–7. Epub 1997/10/07. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

