Natural Products in the "Marketplace": Interfacing Synthesis and Biology
- PMID: 30682249
- PMCID: PMC6446556
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b11297
Natural Products in the "Marketplace": Interfacing Synthesis and Biology
Abstract
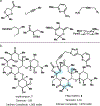
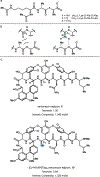
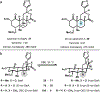
Drugs are discovered through the biological screening of collections of compounds, followed by optimization toward functional end points. The properties of screening collections are often balanced between diversity, physicochemical favorability, intrinsic complexity, and synthetic tractability (Huggins, D. J.; et al. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 208; DOI: 10.1021/cb100420r ). Whereas natural product (NP) collections excel in the first three attributes, NPs suffer a disadvantage on the last point. Academic total synthesis research has worked to solve this problem by devising syntheses of NP leads, diversifying late-stage intermediates, or derivatizing the NP target. This work has led to the discovery of reaction mechanisms, the invention of new methods, and the development of FDA-approved drugs. Few drugs, however, are themselves NPs; instead, NP analogues predominate. Here we highlight past examples of NP analogue development and successful NP-derived drugs. More recently, chemists have explored how NP analogues alter the retrosynthetic analysis of complex scaffolds, merging structural design and synthetic design. This strategy maintains the intrinsic complexity of the NP but can alter the physicochemical properties of the scaffold, like core instability that renders the NP a poor chemotype. Focused libraries based on these syntheses may exclude the NP but maintain the molecular properties that distinguish NP space from synthetic space (Stratton, C. F.; et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4802; DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.014 ), properties that have statistical advantages in clinical progression (Luker, T.; et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5673, DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.07.074 ; Ritchie, T. J.; Macdonald, S. J. F. Drug Discovery Today 2009, 14, 1011, DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2009.07.014 ). Research that expedites synthetic access to NP motifs can prevent homogeneity of chemical matter available for lead discovery. Easily accessed, focused libraries of NP scaffolds can fill empty but active gaps in screening sets and expand the molecular diversity of synthetic collections.
Figures


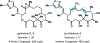

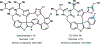

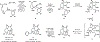
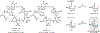

References
-
- Luker T; Alcaraz L; Chohan KK; Blomberg N; Brown DS; Butlin RJ; Elebring T; Griffin AM; Guile S; St-Gallay S; Swahn BM; Swallow S; Waring MJ; Wenlock MC; Leeson PD “Strategies to improve in vivo toxicology outcomes for basic candidate drug molecules Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2011, 21, 5673. - PubMed
-
- Ritchie TJ; Macdonald SJF “The impact of aromatic ring count on compound developability – are too many aromatic rings a liability in drug design?” Drug Disc. Today 2009, 14, 1011. - PubMed
-
- Brazeal Gregory, “How Much Does a Belief Cost?: Revisiting the Marketplace of Ideas” (March 26, 2012). Southern California Interdisciplinary Law Journal, Vol. 21, 2011. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1691952
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

