Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6'-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury
- PMID: 30682785
- PMCID: PMC6387371
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20030502
Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6'-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury
Erratum in
-
Correction: Batsaikhan et al. Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6'-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 502.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Dec 30;27(1):393. doi: 10.3390/ijms27010393. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 41516434 Free PMC article.
Abstract
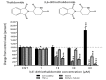
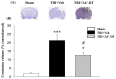
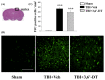
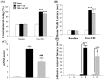
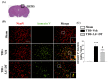
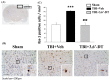
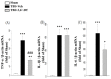
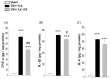
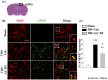
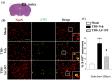
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of mortality and disability worldwide. Long-term deficits after TBI arise not only from the direct effects of the injury but also from ongoing processes such as neuronal excitotoxicity, inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is known to contribute to these processes. We have previously shown that 3,6'-dithiothalidomide (3,6'-DT), a thalidomide analog that is more potent than thalidomide with similar brain penetration, selectively inhibits the synthesis of TNF-α in cultured cells and reverses behavioral impairments induced by mild TBI in mice. In the present study, we further explored the therapeutic potential of 3,6'-DT in an animal model of moderate TBI using Sprague-Dawley rats subjected to controlled cortical impact. A single dose of 3,6'-DT (28 mg/kg, i.p.) at 5 h after TBI significantly reduced contusion volume, neuronal degeneration, neuronal apoptosis and neurological deficits at 24 h post-injury. Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the contusion regions were also suppressed at the transcription and translation level by 3,6'-DT. Notably, neuronal oxidative stress was also suppressed by 3,6'-DT. We conclude that 3,6'-DT may represent a potential therapy to ameliorate TBI-induced functional deficits.
Keywords: 3,6′-dithiothalidomide; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; neurological deficits; oxidative stress; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

