Treatment Combining CD200 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Tumor-Lysate Vaccination after Surgery for Pet Dogs with High-Grade Glioma
- PMID: 30682795
- PMCID: PMC6406711
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11020137
Treatment Combining CD200 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Tumor-Lysate Vaccination after Surgery for Pet Dogs with High-Grade Glioma
Abstract
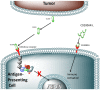
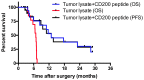
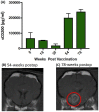
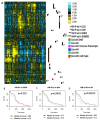
Recent advances in immunotherapy have included inhibition of immune checkpoint proteins in the tumor microenvironment and tumor lysate-based vaccination strategies. We combined these approaches in pet dogs with high-grade glioma. Administration of a synthetic peptide targeting the immune checkpoint protein, CD200, enhanced the capacity of antigen-presenting cells to prime T-cells to mediate an anti-glioma response. We found that in canine spontaneous gliomas, local injection of a canine-specific, CD200-directed peptide before subcutaneous delivery of an autologous tumor lysate vaccine prolonged survival relative to a historical control treated with autologous tumor lysate alone (median survivals of 12.7 months and 6.36 months, respectively). Antigen-presenting cells and T-lymphocytes primed with this peptide suppressed their expression of the inhibitory CD200 receptor, thereby enhancing their ability to initiate immune reactions in a glioblastoma microenvironment replete with the immunosuppressive CD200 protein. These results support consideration of a CD200 ligand as a novel glioblastoma immunotherapeutic agent.
Keywords: dogs; glioma; immunotherapy; tumor lysate.
Conflict of interest statement
Olin and Moertel are co-founders and major shareholders in OX2 Therapeutics.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

