Gut ghrelin regulates hepatic glucose production and insulin signaling via a gut-brain-liver pathway
- PMID: 30683114
- PMCID: PMC6347823
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-019-0321-y
Gut ghrelin regulates hepatic glucose production and insulin signaling via a gut-brain-liver pathway
Abstract
Background: Ghrelin modulates many physiological processes. However, the effects of intestinal ghrelin on hepatic glucose production (HGP) are still unclear. The current study was to explore the roles of intestinal ghrelin on glucose homeostasis and insulin signaling in the liver.
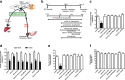
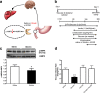
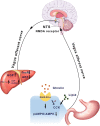
Methods: The system of intraduodenal infusion and intracerebral microinfusion into the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) in the normal chow-diet rats and pancreatic-euglycemic clamp procedure (PEC) combined with [3-3H] glucose as a tracer were used to analyze the effect of intestinal ghrelin. Intraduodenal co-infusion of ghrelin, tetracaine and Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) activator (AICAR), or pharmacologic and molecular inhibitor of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors within the dorsal vagal complex, or hepatic vagotomy in rats were used to explore the possible mechanism of the effect of intestinal ghrelin on HGP.
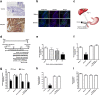
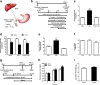
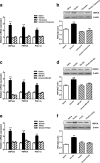
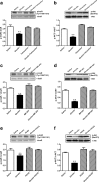
Results: Our results demonstrated that gut infusion of ghrelin inhibited duodenal AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) signal pathways, increased HGP and expression of gluconeogenic enzymes, and decreased insulin signaling in the liver of the rat. Intraduodenal co-infusion of ghrelin receptor antagonist [D-Lys3]-GHRP-6 and AMPK agonist with ghrelin diminished gut ghrelin-induced increase in HGP and decrease in glucose infusion rate (GIR) and hepatic insulin signaling. The effects of gut ghrelin were also negated by co-infusion with tetracaine, or MK801, an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor inhibitor, and adenovirus expressing the shRNA of NR1 subunit of NMDA receptors (Ad-shNR1) within the dorsal vagal complex, and hepatic vagotomy in rats. When ghrelin and lipids were co-infused into the duodenum, the roles of gut lipids in increasing the rate of glucose infusion (GIR) and lowering HGP were reversed.
Conclusions: The current study provided evidence that intestinal ghrelin has an effect on HGP and identified a neural glucoregulatory function of gut ghrelin signaling.
Keywords: Duodenum; Ghrelin; Glucose homeostasis; Insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal study protocols were approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee and Animal Care Committee of Chongqing Medical University.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Duodenal GLP-1 signaling regulates hepatic glucose production through a PKC-δ-dependent neurocircuitry.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Feb 9;8(2):e2609. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.28. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28182013 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin activates a duodenal Ampk-dependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose production in rats.Nat Med. 2015 May;21(5):506-11. doi: 10.1038/nm.3787. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25849133 Free PMC article.
-
Duodenal activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces vagal afferent firing and lowers glucose production in rats.Gastroenterology. 2012 Apr;142(4):834-843.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.053. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22245844
-
Central insulin-mediated regulation of hepatic glucose production [Review].Endocr J. 2016;63(1):1-7. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ15-0540. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Endocr J. 2016. PMID: 26447084 Review.
-
Control of hepatic glucose metabolism by islet and brain.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Sep;16 Suppl 1(0 1):33-40. doi: 10.1111/dom.12332. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 25200294 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the ghrelin system in alcohol use disorder and alcohol-associated liver disease: A narrative review.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2022 Dec;46(12):2149-2159. doi: 10.1111/acer.14967. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2022. PMID: 36316764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enteroendocrine cell regulation of the gut-brain axis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 7;17:1272955. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1272955. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38027512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic ablation of C-reactive protein gene confers resistance to obesity and insulin resistance in rats.Diabetologia. 2021 May;64(5):1169-1183. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05384-9. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33544171
-
Circadian Clock Desynchronization and Insulin Resistance.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 20;20(1):29. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010029. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-organ Coordination of Lipoprotein Secretion by Hormones, Nutrients and Neural Networks.Endocr Rev. 2021 Nov 16;42(6):815-838. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab008. Endocr Rev. 2021. PMID: 33743013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

