Influence of the N-terminal segment and the PHY-tongue element on light-regulation in bacteriophytochromes
- PMID: 30683693
- PMCID: PMC6433076
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007260
Influence of the N-terminal segment and the PHY-tongue element on light-regulation in bacteriophytochromes
Abstract
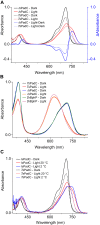
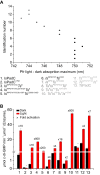
Photoreceptors enable the integration of ambient light stimuli to trigger lifestyle adaptations via modulation of central metabolite levels involved in diverse regulatory processes. Red light-sensing bacteriophytochromes are attractive targets for the development of innovative optogenetic tools because of their natural modularity of coupling with diverse functionalities and the natural availability of the light-absorbing biliverdin chromophore in animal tissues. However, a rational design of such tools is complicated by the poor understanding of molecular mechanisms of light signal transduction over long distances-from the site of photon absorption to the active site of downstream enzymatic effectors. Here we show how swapping structural elements between two bacteriophytochrome homologs provides additional insight into light signal integration and effector regulation, involving a fine-tuned interplay of important structural elements of the sensor, as well as the sensor-effector linker. Facilitated by the availability of structural information of inhibited and activated full-length structures of one of the two homologs (Idiomarina species A28L phytochrome-activated diguanylyl cyclase (IsPadC)) and characteristic differences in photoresponses of the two homologs, we identify an important cross-talk between the N-terminal segment, containing the covalent attachment site of the chromophore, and the PHY-tongue region. Moreover, we highlight how these elements influence the dynamic range of photoactivation and how activation can be improved to light/dark ratios of ∼800-fold by reducing basal dark-state activities at the same time as increasing conversion in the light state. This will enable future optimization of optogenetic tools aiming at a direct allosteric regulation of enzymatic effectors.
Keywords: GGDEF; bilin; cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP); diguanylate cyclase; photobiology; photoreceptor; phytochrome; protein engineering; signal transduction; ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-visible spectroscopy).
© 2019 Gourinchas et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


References
-
- Heintzen C. (2012) Plant and fungal photopigments. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 1, 411–432 10.1002/wmts.36 - DOI
-
- Duanmu D., Bachy C., Sudek S., Wong C.-H., Jiménez V., Rockwell N. C., Martin S. S., Ngan C. Y., Reistetter E. N., van Baren M. J., Price D. C., Wei C. L., Reyes-Prieto A., Lagarias J. C., and Worden A. Z. (2014) Marine algae and land plants share conserved phytochrome signaling systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 15827–15832 10.1073/pnas.1416751111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

