Sources of thymidine and analogs fueling futile damage-repair cycles and ss-gap accumulation during thymine starvation in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 30684682
- PMCID: PMC6382538
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.01.002
Sources of thymidine and analogs fueling futile damage-repair cycles and ss-gap accumulation during thymine starvation in Escherichia coli
Abstract
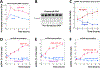
Thymine deprivation in thyA mutant E. coli causes thymineless death (TLD) and is the mode of action of popular antibacterial and anticancer drugs, yet the mechanisms of TLD are still unclear. TLD comprises three defined phases: resistance, rapid exponential death (RED) and survival, with the nature of the resistance phase and of the transition to the RED phase holding key to TLD pathology. We propose that a limited source of endogenous thymine maintains replication forks through the resistance phase. When this source ends, forks undergo futile break-repair cycle during the RED phase, eventually rendering the chromosome non-functional. Two obvious sources of the endogenous thymine are degradation of broken chromosomal DNA and recruitment of thymine from stable RNA. However, mutants that cannot degrade broken chromosomal DNA or lack ribo-thymine, instead of shortening the resistance phase, deepen the RED phase, meaning that only a small fraction of T-starved cells tap into these sources. Interestingly, the substantial chromosomal DNA accumulation during the resistance phase is negated during the RED phase, suggesting futile cycle of incorporation and excision of wrong nucleotides. We tested incorporation of dU or rU, finding some evidence for both, but DNA-dU incorporation accelerates TLD only when intracellular [dUTP] is increased by the dut mutation. In the dut ung mutant, with increased DNA-dU incorporation and no DNA-dU excision, replication is in fact rescued even without dT, but TLD still occurs, suggesting different mechanisms. Finally, we found that continuous DNA synthesis during thymine starvation makes chromosomal DNA increasingly single-stranded, and even the dut ung defect does not completely block this ss-gap accumulation. We propose that instability of single-strand gaps underlies the pathology of thymine starvation.
Keywords: Base excision repair; Chromosomal fragmentation; Chromosomal replication; DNA-dU incorporation; Ribonucleotide excision repair; Thymineless death.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

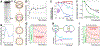
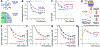

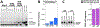


References
-
- Ahmad SI, Kirk SH and Eisenstark A (1998). “Thymine metabolism and thymineless death in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.” Annu. Rev. Microbiol 52: 591–625. - PubMed
-
- An Q, Robins P, Lindahl T and Barnes DE (2007). “5-Fluorouracil incorporated into DNA is excised by the Smug1 DNA glycosylase to reduce drug cytotoxicity.” Cancer Res. 67: 940–945. - PubMed
-
- Barner HD and Cohen SS (1958). “Protein synthesis and RNA turnover in a pyrimidine-deficient bacterium.” Biochim. Biophys. Acta 30: 12–20. - PubMed
-
- Beck CF, Eisenhardt AR and Neuhard J (1975). “Deoxycytidine triphosphate deaminase of Salmonella typhimurium. Purification and characterization.” J. Biol. Chem 250: 609–616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

