Protein expression and function of organic anion transporters in short-term and long-term cultures of Huh7 human hepatoma cells
- PMID: 30685239
- PMCID: PMC6386193
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.01.022
Protein expression and function of organic anion transporters in short-term and long-term cultures of Huh7 human hepatoma cells
Abstract
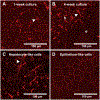
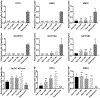
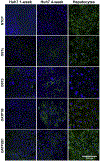
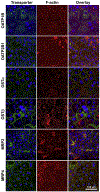
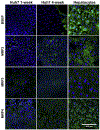
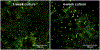
Human-derived hepatic cell lines are a valuable alternative to primary hepatocytes for drug metabolism, transport and toxicity studies. However, their relevance for investigations of drug-drug and drug-organic anion (e.g., bile acid, steroid hormone) interactions at the transporter level remains to be established. The aim of the present study was to determine the suitability of the Huh7 cell line for transporter-dependent experiments. Huh7 cells were cultured for 1 to 4 weeks and subsequently were analyzed for protein expression, localization and activity of solute carrier (SLC) and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters involved in organic anion transport using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopy, immunocytochemistry, and model substrates [3H]taurocholate (TCA), [3H]dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) and 5(6)-carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein (CDF) diacetate. The extended 4-week culture resulted in a phenotype resembling primary hepatocytes and differentiated HepaRG cells: cuboidal hepatocyte-like cells with elongated bile canaliculi-like structures were surrounded by epithelium-like cells. Protein expression of OSTα, OSTβ and OATP1B3 increased over time. Moreover, the uptake of the SLC probe substrate DHEAS was higher in 4-week than in 1-week Huh7 cultures. NTCP, OATP1B1, BSEP and MRP3 were barely or not detectable in Huh7 cells. OATP2B1, MRP2 and MRP4 protein expression remained at similar levels over the four weeks of culture. The activity of MRP2 and the formation of bile canaliculi-like structures were confirmed by accumulation of CDF in the intercellular compartments. Results indicate that along with morphological maturation, transporters responsible for alternative bile acid secretion pathways are expressed and active in long-term cultures of Huh7 cells, suggesting that differentiated Huh7 cells may be suitable for studying the function and regulation of these organic anion transporters.
Keywords: ATP-binding cassette proteins; Hepatocytes; Huh7 cell line; Mass spectrometry; Membrane transport proteins; Phenotype; Solute carrier proteins.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
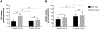
References
-
- Abe T, et al. , 2001. Lst-2, a human liver-specific organic anion transporter, determines methotrexate sensitivity in gastrointestinal cancers. Gastroenterology 120, 1689–1699. - PubMed
-
- Antherieu S, et al. , 2010. Stable expression, activity, and inducibility of cytochromes p450 in differentiated heparg cells. Drug Metab. Dispos 38, 516–525. - PubMed
-
- Arterburn LM, et al. , 1995. A morphological study of differentiated hepatocytes in vitro. Hepatology 22, 175–187. - PubMed
-
- Artursson P, et al. , 2013. In vitro characterization of interactions with drug transporting proteins, in: Sugiyama Y, Steffansen B (Eds.), Transporters in drug development. Springer, New York, NY, AAPS Advances in the Pharmaceutical Sciences Series.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

