Maternal allergen-specific IgG might protect the child against allergic sensitization
- PMID: 30685457
- PMCID: PMC6689269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.11.051
Maternal allergen-specific IgG might protect the child against allergic sensitization
Abstract
Background: Analysis of allergen-specific IgE responses in birth cohorts with microarrayed allergens has provided detailed information regarding the evolution of specific IgE responses in children. High-resolution data regarding early development of allergen-specific IgG are needed.
Objective: We sought to analyze IgG reactivity to microarrayed allergens in mothers during pregnancy, in cord blood samples, in breast milk, and in infants in the first years of life with the aim to investigate whether maternal allergen-specific IgG can protect against IgE sensitization in the offspring.
Methods: Plasma samples from mothers during the third trimester, cord blood, breast milk collected 2 months after delivery, and plasma samples from children at 6, 12, and 60 months of age were analyzed for IgG reactivity to 164 microarrayed allergens (ImmunoCAP ISAC technology) in 99 families of the Swedish birth cohort Assessment of Lifestyle and Allergic Disease During Infancy (ALADDIN). IgE sensitizations to microarrayed allergens were determined at 5 years of age in the children.
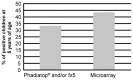
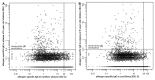
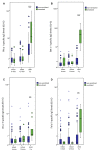
Results: Allergen-specific IgG reactivity profiles in mothers, cord blood, and breast milk were highly correlated. Maternal allergen-specific IgG persisted in some children at 6 months. Children's allergen-specific IgG production occurred at 6 months and reflected allergen exposure. Children who were IgE sensitized against an allergen at 5 years of age had significantly higher allergen-specific IgG levels than nonsensitized children. For all 164 tested allergens, children from mothers with increased (>30 ISAC standardized units) specific plasma IgG levels against an allergen had no IgE sensitizations against that allergen at 5 years of age.
Conclusion: This is the first detailed analysis of the molecular IgG recognition profile in mothers and their children in early life. High allergen-specific IgG reactivity in the mother's plasma and breast milk and in cord blood seemed to protect against allergic sensitization at 5 years of age.
Keywords: Allergy; allergen; allergen-specific IgG; birth cohort; breast milk; cord blood; maternal IgG; microarrayed allergens; recombinant allergen; sensitization.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest: C. Lupinek has received payment for lectures from Thermo Fisher Scientific. H. Hochwallner and R. Valenta have received research grants from the Austrian Science Fund (FWF). R. Valenta has received research grants from Biomay AG, Vienna, Austria, and Viravaxx, Vienna, Austria, and serves as a consultant for these companies. J. Alm has received discounted reagents for this study from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Uppsala, Sweden. The rest of the authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
A role for maternal IgG in protecting infants from allergen-specific IgE sensitization.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Aug;144(2):410-412. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.05.039. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31228475 No abstract available.
-
Reply.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Nov;144(5):1455-1456. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.08.012. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31563342 No abstract available.
-
Does maternal IgG protect infants from allergen-specific IgE sensitization?J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Nov;144(5):1454-1455. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.08.011. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31563343 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kulig M, Bergmann R, Klettke U, Wahn V, Tacke U, Wahn U. Natural course of sensitization to food and inhalant allergens during the first 6 years of life. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:1173–9. - PubMed
-
- Thomas WR. The advent of recombinant allergens and allergen cloning. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:855–9. - PubMed
-
- Valenta R, Ferreira F, Focke-Tejkl M, Linhart B, Niederberger V, Swoboda I, et al. From allergen genes to allergy vaccines. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010;28:211–41. - PubMed
-
- Matricardi PM, Kleine-Tebbe J, Hoffmann HJ, Valenta R, Hilger C, Hofmaier S, et al. EAACI molecular allergology user’s guide. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2016;27(suppl 23):1–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

