Efficacy and patient satisfaction regarding lymphovenous bypass with sleeve-in anastomosis for extremity lymphedema
- PMID: 30685941
- PMCID: PMC6369058
- DOI: 10.5999/aps.2018.00773
Efficacy and patient satisfaction regarding lymphovenous bypass with sleeve-in anastomosis for extremity lymphedema
Abstract
Background: When performing lymphovenous anastomosis, it is sometimes difficult to find venules in the proximity of an ideal lymphatic vessel that have a similar diameter to that of the lymphatic vessel. In this situation, larger venules can be used.
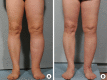
Methods: The authors evaluated the efficacy of and patient satisfaction with lymphovenous bypass with sleeve-in anastomosis. Between January 2014 and December 2016, we performed this procedure in 18 patients (eight upper extremities and 10 lower extremities) with secondary lymphedema. Lymphovenous bypass with sleeve-in anastomosis was performed under microscopy after injecting indocyanine green dye. The circumferential diameter was measured before lymphovenous bypass and at 1, 2, and 6 months after the procedure. An outcomes survey that included patients' qualitative satisfaction with lymphovenous bypass was conducted at 6 months postoperatively.
Results: Almost all patients showed quantitative improvements after surgery. The circumferential reduction rate in patients with stage II lymphedema of both the upper and lower extremities was significantly greater than in their counterparts with stage III/IV lymphedema. The circumferential reduction rate was lower in lower-extremity patients than in upper-extremity patients.
Conclusions: Lymphovenous bypass surgery with sleeve-in anastomosis in lymphedema patients is beneficial, and appears to be effective, when adequately-sized venules cannot be found in the proximity of an ideal lymphatic vessel.
Keywords: Lower extremity; Lymphedema; Microsurgery; Upper extremity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures






References
-
- Campisi C. Lymphoedema: modern diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Int Angiol. 1999;18:14–24. - PubMed
-
- Sakorafas GH, Peros G, Cataliotti L, et al. Lymphedema following axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer. Surg Oncol. 2006;15:153–65. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien BM, Chait LA, Hurwitz PJ. Microlymphatic surgery. Orthop Clin North Am. 1977;8:405–24. - PubMed
-
- Koshima I, Inagawa K, Urushibara K, et al. Paraumbilical perforator flap without deep inferior epigastric vessels. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;102:1052–7. - PubMed
-
- Lasso JM, Perez Cano R. Practical solutions for lymphaticovenous anastomosis. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2013;29:1–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

