Radiation Induces Distinct Changes in Defined Subpopulations of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells in the Adult Hippocampus
- PMID: 30686979
- PMCID: PMC6333747
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.01013
Radiation Induces Distinct Changes in Defined Subpopulations of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells in the Adult Hippocampus
Abstract
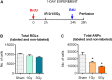
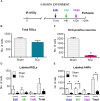
While irradiation can effectively treat brain tumors, this therapy also causes cognitive impairments, some of which may stem from the disruption of hippocampal neurogenesis. To study how radiation affects neurogenesis, we combine phenotyping of subpopulations of hippocampal neural stem and progenitor cells with double- and triple S-phase labeling paradigms. Using this approach, we reveal new features of division, survival, and differentiation of neural stem and progenitor cells after exposure to gamma radiation. We show that dividing neural stem cells, while susceptible to damage induced by gamma rays, are less vulnerable than their rapidly amplifying progeny. We also show that dividing stem and progenitor cells that survive irradiation are suppressed in their ability to replicate 0.5-1 day after the radiation exposure. Suppression of division is also observed for cells that entered the cell cycle after irradiation or were not in the S phase at the time of exposure. Determining the longer term effects of irradiation, we found that 2 months after exposure, radiation-induced suppression of division is partially relieved for both stem and progenitor cells, without evidence for compensatory symmetric divisions as a means to restore the normal level of neurogenesis. By that time, most mature young neurons, born 2-4 weeks after the irradiation, still bear the consequences of radiation exposure, unlike younger neurons undergoing early stages of differentiation without overt signs of deficient maturation. Later, 6 months after an exposure to 5 Gy, cell proliferation and neurogenesis are further impaired, though neural stem cells are still available in the niche, and their pool is preserved. Our results indicate that various subpopulations of stem and progenitor cells in the adult hippocampus have different susceptibility to gamma radiation, and that neurogenesis, even after a temporary restoration, is impaired in the long term after exposure to gamma rays. Our study provides a framework for investigating critical issues of neural stem cell maintenance, aging, interaction with their microenvironment, and post-irradiation therapy.
Keywords: adult neurogenesis; gamma irradiation; nucleotide labeling; quiescent progenitors; stem cells.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

