Orexin Receptor Blockade-Induced Sleep Preserves the Ability to Wake in the Presence of Threat in Mice
- PMID: 30687033
- PMCID: PMC6338018
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00327
Orexin Receptor Blockade-Induced Sleep Preserves the Ability to Wake in the Presence of Threat in Mice
Abstract
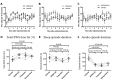
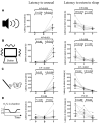
Retention of the ability to wake from sleep in response to dangerous situations is an ideal characteristic of safe hypnotics. We studied the effects of a dual orexin receptor antagonist-22 (DORA-22) and the GABA-A receptor modulator, triazolam, on the ability to wake in response to aversive stimuli. We examined four modalities of sensory inputs, namely, auditory (ultrasonic sound), vestibular (trembling), olfactory (predator odor), and autonomic (hypoxia) stimuli. When the mice fell asleep, one of the four stimuli was applied for 30 s. In the case of auditory stimulation, latency to arousal following vehicle, DORA-22, and triazolam administration was 3.0 (2.0-3.8), 3.5 (2.0-6.5), and 161 (117-267) s (median and 25-75 percentile in the parentheses, n = 8), respectively. Latency to return to sleep after arousal was 148 (95-183), 70 (43-98), and 60 (52-69) s, respectively. Similar results were obtained for vestibular and olfactory stimulation. During the hypoxic stimulation, latencies for arousal and returning to sleep were not significantly different among the groups. The findings of this study are consistent with the distinct mechanisms of these sleep promoting therapies; GABA-A receptor activation by triazolam is thought to induce widespread central nervous system (CNS) suppression while DORA-22 more specifically targets sleep/wake pathways through orexin receptor antagonism. These data support the notion that DORA-22 preserves the ability to wake in response to aversive and consciousness-inducing sensory stimuli, regardless of modality, while remaining effective in the absence of threat. This study provides a unique and important safety evaluation of the potential for certain hypnotics.
Keywords: aversive stimuli; dual orexin receptor antagonist; hypnotics; hypocretin; orexin; triazolam.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orexin receptor antagonist-induced sleep does not impair the ability to wake in response to emotionally salient acoustic stimuli in dogs.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 May 16;8:182. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00182. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24904334 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Orexin Signaling Promotes Sleep Yet Preserves Salient Arousability in Monkeys.Sleep. 2016 Mar 1;39(3):603-12. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5536. Sleep. 2016. PMID: 26943466 Free PMC article.
-
Differential sleep-promoting effects of dual orexin receptor antagonists and GABAA receptor modulators.BMC Neurosci. 2014 Sep 22;15:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-15-109. BMC Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25242351 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep-wake and arousal dysfunctions in post-traumatic stress disorder: Role of orexin systems.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Aug;186:106-122. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.05.006. Epub 2022 May 23. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35618150 Review.
-
Orexin in sleep, addiction and more: is the perfect insomnia drug at hand?Neuropeptides. 2013 Dec;47(6):477-88. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Neuropeptides. 2013. PMID: 24215799 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal Networks in Hypertension: Recent Advances.Hypertension. 2020 Aug;76(2):300-311. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.14521. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32594802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal relationships between sleep and smell.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 Dec 22;16:1076354. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.1076354. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 36619661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Treatment of Chronic Insomnia: A Narrative Review of New Nonpharmacologic and Pharmacologic Therapies.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Aug 6;17:2549-2566. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S297504. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 34393484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can the Orexin Antagonist Suvorexant Preserve the Ability to Awaken to Auditory Stimuli While Improving Sleep?J Clin Sleep Med. 2019 Sep 15;15(9):1285-1291. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.7920. J Clin Sleep Med. 2019. PMID: 31538599 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Mediates Hypoxic Responses in Mice.Front Physiol. 2020 Oct 22;11:576209. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.576209. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33192579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carrive P., Kuwaki T. (2016). “Orexin and central modulation of cardiovascular and respiratory function,” in Behavioral Neuroscience of Orexin/Hypocretin. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences, eds Lawrence A., de Lecea L. (Cham: Springer; ), 157–196. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

