Systems Pharmacology Dissection of Multi-Scale Mechanisms of Action of Huo-Xiang-Zheng-Qi Formula for the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases
- PMID: 30687082
- PMCID: PMC6336928
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01448
Systems Pharmacology Dissection of Multi-Scale Mechanisms of Action of Huo-Xiang-Zheng-Qi Formula for the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases
Abstract
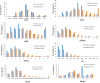
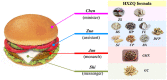
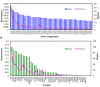
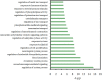
Multi-components Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) treats various complex diseases (multi-etiologies and multi-symptoms) via herbs interactions to exert curative efficacy with less adverse effects. However, the ancient Chinese compatibility theory of herbs formula still remains ambiguous. Presently, this combination principle is dissected through a systems pharmacology study on the mechanism of action of a representative TCM formula, Huo-xiang-zheng-qi (HXZQ) prescription, on the treatment of functional dyspepsia (FD), a chronic or recurrent clinical disorder of digestive system, as typical gastrointestinal (GI) diseases which burden human physical and mental health heavily and widely. In approach, a systems pharmacology platform which incorporates the pharmacokinetic and pharmaco-dynamics evaluation, target fishing and network pharmacological analyses is employed. As a result, 132 chemicals and 48 proteins are identified as active compounds and FD-related targets, and the mechanism of HXZQ formula for the treatment of GI diseases is based on its three function modules of anti-inflammation, immune protection and gastrointestinal motility regulation mainly through four, i.e., PIK-AKT, JAK-STAT, Toll-like as well as Calcium signaling pathways. In addition, HXZQ formula conforms to the ancient compatibility rule of "Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi" due to the different, while cooperative roles that herbs possess, specifically, the direct FD curative effects of GHX (serving as Jun drug), the anti-bacterial efficacy and major accompanying symptoms-reliving bioactivities of ZS and BZ (as Chen), the detoxication and ADME regulation capacities of GC (as Shi), as well as the minor symptoms-treating efficacy of the rest 7 herbs (as Zuo). This work not only provides an insight of the therapeutic mechanism of TCMs on treating GI diseases from a multi-scale perspective, but also may offer an efficient way for drug discovery and development from herbal medicine as complementary drugs.
Keywords: Huo-xiang-zheng-qi; TCM; compatibility theory; functional dyspepsia; gastrointestinal diseases; systems pharmacology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and quality control of isomers in Huo-Xiang-Zheng-Qi Mixture using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and inductive effects analysis.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2025 Mar 15;255:116646. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116646. Epub 2024 Dec 18. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2025. PMID: 39718270
-
Protective Effects of Huo Xiang Zheng Qi Liquid on Clostridioides difficile Infection on C57BL/6 Mice.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):1602. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081602. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203444 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of non-targeted multicomponent profiling, targeted characteristic chromatograms and quantitative to accomplish systematic quality evaluation strategy of Huo-Xiang-Zheng-Qi oral liquid.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023 Nov 30;236:115715. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115715. Epub 2023 Sep 11. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023. PMID: 37769526
-
Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumae formula for application to cardiovascular disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jan 9;145(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.09.051. Epub 2012 Nov 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23142198 Review.
-
Systems Pharmacology for Investigation of the Mechanisms of Action of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Drug Discovery.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 11;10:743. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00743. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31379563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A study of the therapeutic mechanism of Jakyakgamcho-Tang about functional dyspepsia through network pharmacology research.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Oct 17;19(13):1824-1834. doi: 10.7150/ijms.77451. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36438925 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicines in Functional Gastrointestinal and Motility Disorders.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2022 Mar;24(3):43-51. doi: 10.1007/s11894-022-00843-8. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35353338 Review.
-
Systematic identification of the interventional mechanism of Qingfei Xiaoyan Wan (QFXYW) in treatment of the cytokine storm in acute lung injury using transcriptomics-based system pharmacological analyses.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):743-754. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2055090. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35357989 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Chinese Pharmacopoeia in the Evaluation and Treatment of COVID-19.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(14):1060-1074. doi: 10.2174/0113816128217263240220060252. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38523518 Review.
-
Huoxiang Zhengqi alleviates azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis-associated cancer by regulating Nrf2/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1002269. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1002269. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andeol Y., Bonneau J. M., Gagne L., Jacquet K., Rivest V., Huot M., et al. (2018). The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) positively regulate the activity of metal-responsive transcription factor-1 (MTF-1) in response to zinc ions. Biochem. Cell Biol. 10.1139/bcb-2018-0073 [Epub ahead of print]. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

