Contribution of Nrf2 Modulation to the Mechanism of Action of Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Drugs in Pre-clinical and Clinical Stages
- PMID: 30687097
- PMCID: PMC6337248
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01536
Contribution of Nrf2 Modulation to the Mechanism of Action of Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Drugs in Pre-clinical and Clinical Stages
Abstract
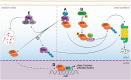
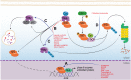
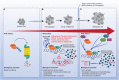
Despite the progress that has occurred in recent years in the development of therapies to treat painful and inflammatory diseases, there is still a need for effective and potent analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. It has long been known that several types of antioxidants also possess analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, indicating a strong relationship between inflammation and oxidative stress. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of action of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, as well as essential targets in disease physiopathology, is essential to the development of novel therapeutic strategies. The Nuclear factor-2 erythroid related factor-2 (Nrf2) is a transcription factor that regulates cellular redox status through endogenous antioxidant systems with simultaneous anti-inflammatory activity. This review summarizes the molecular mechanisms and pharmacological actions screened that link analgesic, anti-inflammatory, natural products, and other therapies to Nrf2 as a regulatory system based on emerging evidences from experimental disease models and new clinical trial data.
Keywords: Keap1; Nrf2; analgesic; anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; inflammation; oxidative stress; pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diosmetin alleviates neuropathic pain by regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jan;170:116067. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116067. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38150877
-
Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis: insights into NRF2-KEAP1 signalling.Autoimmunity. 2021 Nov;54(7):385-397. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1963959. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Autoimmunity. 2021. PMID: 34415206 Review.
-
The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effect of a classical hypnotic bromovalerylurea mediated by the activation of NRF2.J Biochem. 2023 Jul 31;174(2):131-142. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvad030. J Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37039781 Free PMC article.
-
New advances in Nrf2-mediated analgesic drugs.Phytomedicine. 2023 Feb;110:154598. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154598. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36603339 Review.
-
Polydatin prevents fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition through increasing miR-200a to regulate Keap1/Nrf2 pathway.Redox Biol. 2018 Sep;18:124-137. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 30014902 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Accumulation of Cisplatin in Ovarian Cancer Cells from Combination with Wedelolactone and Resulting Inhibition of Multiple Epigenetic Drivers.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 May 25;15:2211-2227. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S288707. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34079223 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Reverses 10-Hydroxycamptothecin-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy in Mouse Oocyte.Reprod Sci. 2021 Jul;28(7):1839-1849. doi: 10.1007/s43032-020-00359-4. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Reprod Sci. 2021. PMID: 33104985
-
Chronic Exposure to the Food Additive tBHQ Modulates Expression of Genes Related to SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza Viruses.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 26;12(5):642. doi: 10.3390/life12050642. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629310 Free PMC article.
-
Apomorphine Reduces A53T α-Synuclein-Induced Microglial Reactivity Through Activation of NRF2 Signalling Pathway.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;42(8):2673-2695. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01131-1. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34415465 Free PMC article.
-
Rutin: a pain-relieving flavonoid.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Mar;33(3):1289-1301. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01671-8. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39961908 Review.
References
-
- Alam M. M., Okazaki K., Nguyen L. T. T., Ota N., Kitamura H., Murakami S., et al. (2017). Glucocorticoid receptor signaling represses the antioxidant response by inhibiting histone acetylation mediated by the transcriptional activator NRF2. J. Biol. Chem. 292 7519–7530. 10.1074/jbc.M116.773960 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

