Medical and surgical management of acute spinal injury during pregnancy: A case series in a third-world country
- PMID: 30687569
- PMCID: PMC6322169
- DOI: 10.4103/sni.sni_380_18
Medical and surgical management of acute spinal injury during pregnancy: A case series in a third-world country
Abstract
Background: There is scant literature describing the management of acute spinal injury in pregnant patients. Here, we report our experience with five cases of pregnant patients including three females who suffered acute traumatic spinal cord injuries (SCIs).
Methods: This retrospective study evaluated five pregnant women presenting with traumatic spinal injuries over a 16-month period. All were assessed using the International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Patients and the American Spine Injury Association Impairment Scale (AIS).
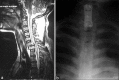
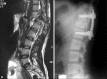
Results: Three patients sustained SCIs: two cervical spine (C4 AIS-A and C5 AIS-B) and one thoracolumbar junction fracture dislocation (T11 AIS-A). Two patients required surgical stabilization during pregnancy, with one undergoing surgery after delivery. All three patients subsequently delivered healthy newborns. The remaining two patients without neurologic deficits at admission were treated conservatively; one had a healthy child, whereas the other patient aborted the baby due to the initial trauma.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that the same surgical principals may be applied to pregnant women as to routine patients with SCIs. Further studies with greater patient data should be performed to better develop significant guidelines for the management of pregnant patients with spinal injuries.
Keywords: Autonomic dysreflexia; management; pregnancy; spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cervical spine injury from gunshot wounds.J Neurosurg Spine. 2014 Sep;21(3):442-9. doi: 10.3171/2014.5.SPINE13522. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014. PMID: 24926931
-
Functional Outcomes in Individuals Undergoing Very Early (< 5 h) and Early (5-24 h) Surgical Decompression in Traumatic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury: Analysis of Neurological Improvement from the Austrian Spinal Cord Injury Study.J Neurotrauma. 2017 Dec 15;34(24):3362-3371. doi: 10.1089/neu.2017.5132. Epub 2017 Aug 10. J Neurotrauma. 2017. PMID: 28683592
-
First aid and treatment for cervical spinal cord injury with fracture and dislocation.Indian J Orthop. 2007 Oct;41(4):300-4. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.36991. Indian J Orthop. 2007. PMID: 21139782 Free PMC article.
-
Update on critical care for acute spinal cord injury in the setting of polytrauma.Neurosurg Focus. 2017 Nov;43(5):E19. doi: 10.3171/2017.7.FOCUS17396. Neurosurg Focus. 2017. PMID: 29088951 Review.
-
Traumatic cervical spine spondyloptosis: A systematic review.J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2022 Jan-Mar;13(1):9-16. doi: 10.4103/jcvjs.jcvjs_132_21. Epub 2022 Mar 9. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2022. PMID: 35386237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spinal cord injury during early pregnancy: Problems in the course of rehabilitation and infant care, a case report.J Spinal Cord Med. 2023 Jul;46(4):692-696. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2021.1965336. Epub 2021 Nov 2. J Spinal Cord Med. 2023. PMID: 34726586 Free PMC article.
-
Obstetric Outcomes of Women Who Sustained Traumatic Spinal Injury during Pregnancy: A Systematic Review.Asian Spine J. 2022 Apr;16(2):290-300. doi: 10.31616/asj.2020.0192. Epub 2021 May 6. Asian Spine J. 2022. PMID: 33940772 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of different surgical methods in the treatment of acute central cord syndrome without fractures and dislocations of the cervical spine.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(1):71-77. doi: 10.3233/BMR-210377. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 35988214 Free PMC article.
-
[The (severely) injured pregnant patient from the perspective of trauma surgery].Unfallchirurg. 2020 Dec;123(12):911-921. doi: 10.1007/s00113-020-00868-6. Unfallchirurg. 2020. PMID: 32955671 German.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
