Childhood Vasculitis
- PMID: 30687686
- PMCID: PMC6335362
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2018.00421
Childhood Vasculitis
Abstract
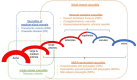
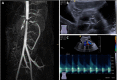
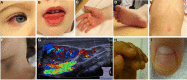
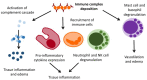
The term vasculitis covers heterogeneous disorders that share the presence of inflammation of blood vessel walls. Immune cell infiltrates can vary significantly and involve granulocytes or mononuclear cells. Vasculitis can be a symptom of other underlying disorders or the underlying cause of organ specific or systemic disease. Classification of childhood vasculitis is based on clinic, the size of predominantly affected vessels, and the histopathology of inflammatory infiltrates. Timely and accurate diagnosis and (where necessary) treatment initiation determine disease progression and outcomes. In light of new developments and the identification of autoinflammatory conditions with vasculitis, new classification tools may be discussed.
Keywords: classification; granulomatosis with polyangitis; inflammation; kawasaki disease; paediatric; purpura; systemic disease; vasculitis.
Figures
References
-
- Ozen S, Pistorio A, Iusan SM, Bakkaloglu A, Herlin T, Brik R, et al. EULAR/PRINTO/PRES criteria for Henoch-Schonlein purpura, childhood polyarteritis nodosa, childhood Wegener granulomatosis and childhood Takayasu arteritis: Ankara 2008. Part II: final classification criteria. Ann Rheum Dis. (2010) 69:798–806. 10.1136/ard.2009.116657 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ruperto N, Ozen S, Pistorio A, Dolezalova P, Brogan P, Cabral DA, et al. EULAR/PRINTO/PRES criteria for Henoch-Schonlein purpura, childhood polyarteritis nodosa, childhood Wegener granulomatosis and childhood Takayasu arteritis: Ankara 2008. Part I: overall methodology and clinical characterisation. Ann Rheum Dis. (2010) 69:790–7. 10.1136/ard.2009.116624 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

