The Effects of Exercise Regimens on Irisin Levels in Obese Rats Model: Comparing High-Intensity Intermittent with Continuous Moderate-Intensity Training
- PMID: 30687746
- PMCID: PMC6327284
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4708287
The Effects of Exercise Regimens on Irisin Levels in Obese Rats Model: Comparing High-Intensity Intermittent with Continuous Moderate-Intensity Training
Abstract
Background: Recently, high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT) appears to have the same beneficial effects or even superior to those of continuous moderate-intensity training (CMIT) on body fat mass reduction. Exercise may induce myokine secretion such as irisin, which plays a role as a mediator of beiging process, and thus might contribute as treatment of obesity. However, the effects of those exercise formulas on irisin level changes as beiging agent are not known. In addition, metabolic states may affect the irisin responses to those exercise formulas. Therefore, this study was aimed to determine the different effects of exercises using HIIT and CMIT on circulating and tissue irisin levels in normal and abnormal metabolic conditions (obese).
Methods: Sixteen male Sprague-Dawley rats (8 weeks of age) were randomized to 4 groups according to training regimens (HIIT and CMIT) and metabolic conditions (normal and abnormal/obese). The groups are (1) HIIT on normal metabolic (n=4), (2) CMIT on normal metabolic (n=4), (3) HIIT on abnormal metabolic (n=4), and (4) CMIT on abnormal metabolic (n=4). Abnormal metabolic condition was induced with high fat diet (19% fat) for 8 weeks in obese rats. Irisin levels in serum, skeletal muscle, and white adipose tissue were evaluated by ELISA.
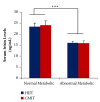
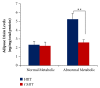
Results: Serum irisin levels were shown significantly higher in normal metabolic compared to abnormal metabolic condition (P<0.001). The effect of interaction between metabolic condition and exercise formula was found (P<0.01) on adipose irisin levels. The effect of HIIT was shown significantly more effective on adipose irisin levels, compared with CMIT in abnormal metabolic conditions. However, no significant differences of skeletal muscle irisin levels were found in both normal and abnormal metabolic subjects (P>0.05). Regarding exercise formula, no different effects were found between HIIT and CMIT on skeletal muscle irisin levels in both metabolic conditions (P>0.05). The similar findings were observed in serum irisin levels (P>0.05).
Conclusions: The exercise effects in abnormal metabolic condition might be more adaptable in maintaining the irisin levels in skeletal muscle and induce the irisin uptake from circulation into adipose tissue. In addition, HIIT might be more involved to induce irisin uptake into adipose tissue; thus it might have the significant role in beiging process. However, further research about how the HIIT formula affects the regulation mechanisms of irisin uptake into adipose tissue is still warranted.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metabolic cross-talk between skeletal muscle and adipose tissue in high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training by regulation of PGC-1α.Eat Weight Disord. 2020 Feb;25(1):17-24. doi: 10.1007/s40519-018-0491-4. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Eat Weight Disord. 2020. PMID: 29480414
-
High-intensity interval versus moderate-intensity continuous training: Superior metabolic benefits in diet-induced obesity mice.Life Sci. 2017 Dec 15;191:122-131. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.023. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28843495
-
Treating fructose-induced metabolic changes in mice with high-intensity interval training: insights in the liver, white adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Oct 1;123(4):699-709. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00154.2017. Epub 2017 May 11. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 28495843
-
Exercise-Induced Irisin, the Fat Browning Myokine, as a Potential Anticancer Agent.J Obes. 2019 Apr 1;2019:6561726. doi: 10.1155/2019/6561726. eCollection 2019. J Obes. 2019. PMID: 31065382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of High-intensity Interval Training vs Moderate-intensity Continuous Training on Liver Fat: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Feb 17;107(3):862-881. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab795. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 34724062
Cited by
-
Potential of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. in managing FGF21 resistance in diet-induced-obesity rats via miR-34a regulation.Vet Med Sci. 2022 Jan;8(1):309-317. doi: 10.1002/vms3.653. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Vet Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34687158 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Roles in Neuroprotection for the Exercise Derived Myokine Irisin.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Apr 16;13:649929. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.649929. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33935687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Handful of Details to Ensure the Experimental Reproducibility on the FORCED Running Wheel in Rodents: A Systematic Review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 10;12:638261. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.638261. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34040580 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships Between Circulating Irisin Response to Ice Swimming and Body Composition in People With Regular Exercise Experience.Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 13;11:596896. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.596896. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33519505 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical Stimulation Protects Against Chondrocyte Pyroptosis Through Irisin-Induced Suppression of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signal Pathway in Osteoarthritis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 9;10:797855. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.797855. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35356271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perakakis N., Triantafyllou G. A., Fernández-Real J. M., et al. Physiology and role of irisin in glucose homeostasis. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2017;13(6):324–337. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.221. http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nrendo.2016.221..... - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

