Effect of Intensive vs Standard Blood Pressure Control on Probable Dementia: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 30688979
- PMCID: PMC6439590
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.21442
Effect of Intensive vs Standard Blood Pressure Control on Probable Dementia: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: There are currently no proven treatments to reduce the risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia.
Objective: To evaluate the effect of intensive blood pressure control on risk of dementia.
Design, setting, and participants: Randomized clinical trial conducted at 102 sites in the United States and Puerto Rico among adults aged 50 years or older with hypertension but without diabetes or history of stroke. Randomization began on November 8, 2010. The trial was stopped early for benefit on its primary outcome (a composite of cardiovascular events) and all-cause mortality on August 20, 2015. The final date for follow-up of cognitive outcomes was July 22, 2018.
Interventions: Participants were randomized to a systolic blood pressure goal of either less than 120 mm Hg (intensive treatment group; n = 4678) or less than 140 mm Hg (standard treatment group; n = 4683).
Main outcomes and measures: The primary cognitive outcome was occurrence of adjudicated probable dementia. Secondary cognitive outcomes included adjudicated mild cognitive impairment and a composite outcome of mild cognitive impairment or probable dementia.
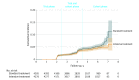
Results: Among 9361 randomized participants (mean age, 67.9 years; 3332 women [35.6%]), 8563 (91.5%) completed at least 1 follow-up cognitive assessment. The median intervention period was 3.34 years. During a total median follow-up of 5.11 years, adjudicated probable dementia occurred in 149 participants in the intensive treatment group vs 176 in the standard treatment group (7.2 vs 8.6 cases per 1000 person-years; hazard ratio [HR], 0.83; 95% CI, 0.67-1.04). Intensive BP control significantly reduced the risk of mild cognitive impairment (14.6 vs 18.3 cases per 1000 person-years; HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.69-0.95) and the combined rate of mild cognitive impairment or probable dementia (20.2 vs 24.1 cases per 1000 person-years; HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.74-0.97).
Conclusions and relevance: Among ambulatory adults with hypertension, treating to a systolic blood pressure goal of less than 120 mm Hg compared with a goal of less than 140 mm Hg did not result in a significant reduction in the risk of probable dementia. Because of early study termination and fewer than expected cases of dementia, the study may have been underpowered for this end point.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01206062.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Prevention of Cognitive Impairment With Intensive Systolic Blood Pressure Control.JAMA. 2019 Feb 12;321(6):548-549. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0008. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 30688980 No abstract available.
-
Blood pressure and dementia: What the SPRINT-MIND trial adds and what we still need to know.Neurology. 2019 May 21;92(21):1017-1018. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007543. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Neurology. 2019. PMID: 31019101 No abstract available.
-
Analysis of Long-term Benefits of Intensive Blood Pressure Control.JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):169-170. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.5840. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31287515 No abstract available.
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):1269-1324. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000066 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

