Identification of an active miniature inverted-repeat transposable element mJing in rice
- PMID: 30689248
- PMCID: PMC6850418
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.14260
Identification of an active miniature inverted-repeat transposable element mJing in rice
Abstract
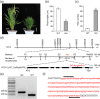
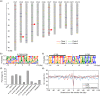
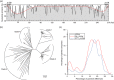
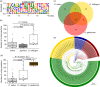
Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) are structurally homogeneous non-autonomous DNA transposons with high copy numbers that play important roles in genome evolution and diversification. Here, we analyzed the rice high-tillering dwarf (htd) mutant in an advanced backcross population between cultivated and wild rice, and identified an active MITE named miniature Jing (mJing). The mJing element belongs to the PIF/Harbinger superfamily. japonica rice var. Nipponbare and indica var. 93-11 harbor 72 and 79 mJing family members, respectively, have undergone multiple rounds of amplification bursts during the evolution of Asian cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). A heterologous transposition experiment in Arabidopsis thaliana indicated that the autonomous element Jing is likely to have provides the transposase needed for mJing mobilization. We identified 297 mJing insertion sites and their presence/absence polymorphism among 71 rice samples through targeted high-throughput sequencing. The results showed that the copy number of mJing varies dramatically among Asian cultivated rice (O. sativa), its wild ancestor (O. rufipogon), and African cultivated rice (O. glaberrima) and that some mJing insertions are subject to directional selection. These findings suggest that the amplification and removal of mJing elements have played an important role in rice genome evolution and species diversification.
Keywords: DNA transposon; MITE; amplification; rice; targeted high-throughput sequencing.
© 2019 The Authors. The Plant Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) have been accumulated through amplification bursts and play important roles in gene expression and species diversity in Oryza sativa.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Mar;29(3):1005-17. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr282. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22096216 Free PMC article.
-
Transposition of the rice miniature inverted repeat transposable element mPing in Arabidopsis thaliana.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 26;104(26):10962-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702080104. Epub 2007 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17578919 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Miniature Inverted-Repeat Transposable Elements by Targeted High-Throughput Sequencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2250:75-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1134-0_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33900593
-
Using rice to understand the origin and amplification of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs).Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004 Apr;7(2):115-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.01.004. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004. PMID: 15003209 Review.
-
Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements: discovery, distribution, and activity.Genome. 2013 Sep;56(9):475-86. doi: 10.1139/gen-2012-0174. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Genome. 2013. PMID: 24168668 Review.
Cited by
-
Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs), derived insertional polymorphism as a tool of marker systems for molecular plant breeding.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Apr;47(4):3155-3167. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05365-y. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32162128 Review.
-
Discovery and genome-wide characterization of a novel miniature inverted repeat transposable element reveal genome-specific distribution in Glycine.Genes Genomics. 2024 Nov;46(11):1271-1280. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01519-5. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38676850
-
Identification of Transposable Elements in Conifer and Their Potential Application in Breeding.Evol Bioinform Online. 2020 Jun 15;16:1176934320930263. doi: 10.1177/1176934320930263. eCollection 2020. Evol Bioinform Online. 2020. PMID: 32595272 Free PMC article.
-
Stowaway miniature inverted repeat transposable elements are important agents driving recent genomic diversity in wild and cultivated carrot.Mob DNA. 2019 Nov 27;10:47. doi: 10.1186/s13100-019-0190-3. eCollection 2019. Mob DNA. 2019. PMID: 31798695 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variability of aquaporin expression in maize: From eQTLs to a MITE insertion regulating PIP2;5 expression.Plant Physiol. 2024 Sep 2;196(1):368-384. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae326. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38839061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennetzen, J.L. and Wang, H. (2014) The contributions of transposable elements to the structure, function, and evolution of plant genomes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 65, 505–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

