Metagenomic quorum quenching enzymes affect biofilm formation of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 30689669
- PMCID: PMC6349329
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211366
Metagenomic quorum quenching enzymes affect biofilm formation of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
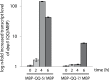
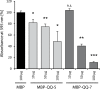
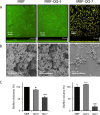
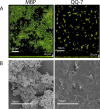
Biofilm formation in the clinical environment is of increasing concern since a significant part of human infections is associated, and caused by biofilm establishment of (opportunistic) pathogens, for instance Candida albicans and Staphylococcus epidermidis. The rapidly increasing number of antibiotic-resistant biofilms urgently requires the development of novel and effective strategies to prevent biofilm formation ideally targeting a wide range of infectious microorganisms. Both, synthesis of extracellular polymeric substances and quorum sensing are crucial for biofilm formation, and thus potential attractive targets to combat undesirable biofilms.We evaluated the ability of numerous recently identified metagenome-derived bacterial quorum quenching (QQ) proteins to inhibit biofilm formation of C. albicans and S. epidermidis. Here, proteins QQ-5 and QQ-7 interfered with the morphogenesis of C. albicans by inhibiting the yeast-to-hyphae transition, ultimately leading to impaired biofilm formation. Moreover, QQ5 and QQ-7 inhibited biofilm formation of S. epidermidis; in case of QQ7 most likely due to induced expression of the icaR gene encoding the repressor for polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) synthesis, the main determinant for staphylococcal biofilm formation. Our results indicate that QQ-5 and QQ-7 are attractive potential anti-biofilm agents in the prevention and treatment of C. albicans and S. epidermidis mono-species biofilms, and potentially promising anti-biofilm drugs in also combating multi-species infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[FUNCTION OF INTERCELLULAR ADHESION A, FIBRINOGEN BINDING PROTEIN, AND ACCUMULATION-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN GENES IN FORMATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS EPIDERMIDIS-CANDIDA ALBICANS MIXED SPECIES BIOFILMS].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Jan;29(1):63-8. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26455175 Chinese.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 10;5:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25713785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The small non-coding RNA RsaE influences extracellular matrix composition in Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm communities.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Mar 14;15(3):e1007618. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007618. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30870530 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin or protein factors in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from prosthetic hip and knee joint infections.Biomaterials. 2007 Mar;28(9):1711-20. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.11.046. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Biomaterials. 2007. PMID: 17187854
-
Molecular genetics of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms on indwelling medical devices.Int J Artif Organs. 2005 Nov;28(11):1069-78. doi: 10.1177/039139880502801104. Int J Artif Organs. 2005. PMID: 16353113 Review.
Cited by
-
The Bovhyaluronidase Azoximer (Longidaza®) Disrupts Candida albicans and Candida albicans-Bacterial Mixed Biofilms and Increases the Efficacy of Antifungals.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Nov 23;58(12):1710. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121710. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36556912 Free PMC article.
-
The Oral Microbiota: Community Composition, Influencing Factors, Pathogenesis, and Interventions.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 29;13:895537. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.895537. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35572634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candida albicans and Staphylococcus Species: A Threatening Twosome.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 18;10:2162. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02162. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31620113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofilms in Surgical Site Infections: Recent Advances and Novel Prevention and Eradication Strategies.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;11(1):69. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010069. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dental tray adhesives and their role as potential transmission medium for microorganisms.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2021 Oct;7(5):829-832. doi: 10.1002/cre2.432. Epub 2021 May 6. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2021. PMID: 33955697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rupp ME, Archer GL. Coagulase-negative staphylococci: pathogens associated with medical progress. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 1994:231–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

