Global Review of the Age Distribution of Rotavirus Disease in Children Aged <5 Years Before the Introduction of Rotavirus Vaccination
- PMID: 30689799
- PMCID: PMC6736387
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz060
Global Review of the Age Distribution of Rotavirus Disease in Children Aged <5 Years Before the Introduction of Rotavirus Vaccination
Abstract
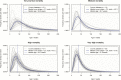
We sought datasets with granular age distributions of rotavirus-positive disease presentations among children <5 years of age, before the introduction of rotavirus vaccines. We identified 117 datasets and fit parametric age distributions to each country dataset and mortality stratum. We calculated the median age and the cumulative proportion of rotavirus gastroenteritis events expected to occur at ages between birth and 5.0 years. The median age of rotavirus-positive hospital admissions was 38 weeks (interquartile range [IQR], 25-58 weeks) in countries with very high child mortality and 65 weeks (IQR, 40-107 weeks) in countries with very low or low child mortality. In countries with very high child mortality, 69% of rotavirus-positive admissions in children <5 years of age were in the first year of life, with 3% by 10 weeks, 8% by 15 weeks, and 27% by 26 weeks. This information is critical for assessing the potential benefits of alternative rotavirus vaccination schedules in different countries and for monitoring program impact.
Keywords: age distribution; rotavirus; rotavirus gastroenteritis; vaccine.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Pneumonia and diarrhea progress report 2017: pushing progress through investment & action Available at: https://www.jhsph.edu/research/centers-and-institutes/ivac/resources/IVA.... Accessed 31 August 2018.
-
- World Health Organization. Table 1: Summary of WHO position papers—recommendations for routine immunization 2018. Available at: https://www.who.int/immunization/policy/Immunization_routine_table1.pdf?.... Accessed 10 January 2019.
-
- Lamberti LM, Ashraf S, Walker CL, Black RE. A systematic review of the effect of rotavirus vaccination on diarrhea outcomes among children younger than 5 years. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2016; 35:992–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

