The long and the short of it: the MDM4 tail so far
- PMID: 30689920
- PMCID: PMC6478121
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz007
The long and the short of it: the MDM4 tail so far
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to 'The long and the short of it: the MDM4 tail so far'.J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Dec 19;11(12):1104. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz109. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31881081 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
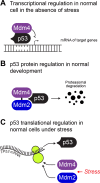
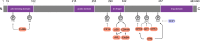
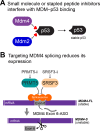
The mouse double minute 4 (MDM4) is emerging from the shadow of its more famous relative MDM2 and is starting to steal the limelight, largely due to its therapeutic possibilities. MDM4 is a vital regulator of the tumor suppressor p53. It restricts p53 transcriptional activity and also, at least in development, facilitates MDM2's E3 ligase activity toward p53. These functions of MDM4 are critical for normal cell function and a proper response to stress. Their importance for proper cell maintenance and proliferation identifies them as a risk for deregulation associated with the uncontrolled growth of cancer. MDM4 tails are vital for its function, where its N-terminus transactivation domain engages p53 and its C-terminus RING domain binds to MDM2. In this review, we highlight recently identified cellular functions of MDM4 and survey emerging therapies directed to correcting its dysregulation in disease.
Keywords: MDM2; MDM4; MDM4-FL; MDM4-S; MDMX; cancer; p53.
© The Author(s) (2019). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, IBCB, SIBS, CAS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dependence on Mdm2 for Mdm4 inhibition of p53 activity.Cancer Lett. 2025 Jul 1;621:217622. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217622. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40081463
-
Structure and function of MDM2 and MDM4 in health and disease.Biochem J. 2025 Feb 17;482(4):BCJ20240757. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240757. Biochem J. 2025. PMID: 39960347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mouse p53 mutant lacking the proline-rich domain rescues Mdm4 deficiency and provides insight into the Mdm2-Mdm4-p53 regulatory network.Cancer Cell. 2006 Apr;9(4):273-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.03.014. Cancer Cell. 2006. PMID: 16616333
-
Novel Inhibitors for MDM2-MDM4 E3 Ligase Potently Induce p53-Indepedent Apoptosis in Drug-Resistant Leukemic Cells.Molecules. 2025 Jan 5;30(1):186. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010186. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39795242 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of Mdm2 and Mdm4 and their clinical implications.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Jul;32(7):371-5. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10286. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23327795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acquisition of chromosome 1q duplication in parental and genome-edited human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem cells results in their higher proliferation rate in vitro and in vivo.Cell Prolif. 2020 Oct;53(10):e12892. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12892. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32918782 Free PMC article.
-
RPL22 is a tumor suppressor in MSI-high cancers and a key splicing regulator of MDM4.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 10:2023.12.10.570873. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.10.570873. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114622. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114622. PMID: 38106152 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CDK4/6 inhibition in cancer: the cell cycle splicing connection.Mol Cell Oncol. 2019 Oct 17;6(6):e1673643. doi: 10.1080/23723556.2019.1673643. eCollection 2019. Mol Cell Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31692881 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Potential miRNAs, as Biomarkers for Sepsis and Associated Lung Injury: A Network-Based Approach.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 10;11(11):1327. doi: 10.3390/genes11111327. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33182754 Free PMC article.
-
p53: updates on mechanisms, biology and therapy (I).J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):185-186. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz017. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31222355 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bardot B., Bouarich-Bourimi R., Leemput J., et al. (2015). Mice engineered for an obligatory Mdm4 exon skipping express higher levels of the Mdm4-S isoform but exhibit increased p53 activity. Oncogene 34, 2943–2948. - PubMed
-
- Bardot B., and Toledo F. (2017). Targeting MDM4 splicing in cancers. Genes 8, pii: E82.
-
- Bartel F., Schulz J., Bohnke A., et al. (2005). Significance of HDMX-S (or MDM4) mRNA splice variant overexpression and HDMX gene amplification on primary soft tissue sarcoma prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 117, 469–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

