Evaluation of apramycin against spectinomycin-resistant and -susceptible strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 30689929
- PMCID: PMC6477976
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkz012
Evaluation of apramycin against spectinomycin-resistant and -susceptible strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
Background: The emergence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae resistant to all currently available antimicrobial therapies poses a dire public health threat. New antimicrobial agents with activity against N. gonorrhoeae are urgently needed. Apramycin is an aminocyclitol aminoglycoside with broad-spectrum in vitro activity against MDR Gram-negative pathogens and Staphylococcus aureus. However, its activity against N. gonorrhoeae has not been described.
Objectives: The activity spectrum of apramycin against a collection of MDR N. gonorrhoeae was assessed. Isolates tested included those susceptible and resistant to the structurally distinct aminocyclitol, spectinomycin.
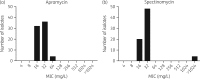
Results: The modal MICs for apramycin and spectinomycin were 16 mg/L and 32 mg/L, respectively. The epidemiological cut-off (ECOFF) for apramycin was 64 mg/L. No strains among 77 tested had an MIC above this ECOFF, suggesting very low levels of acquired apramycin resistance. In time-kill analysis, apramycin demonstrated rapid bactericidal activity comparable to that of spectinomycin.
Conclusions: Apramycin has broad-spectrum, rapidly bactericidal activity against N. gonorrhoeae. Future pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies will be needed to determine whether apramycin and/or apramycin derivatives hold promise as new therapeutics for N. gonorrhoeae infection.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Lewis DA. The Gonococcus fights back: is this time a knock out? Sex Transm Infect 2010; 86: 415–21. - PubMed
-
- Tapsall JW, Ndowa F, Lewis DA. et al. Meeting the public health challenge of multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2009; 7: 821–34. - PubMed
-
- Cole MJ, Chisholm SA, Hoffmann S. et al. European surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Sex Transm Infect 2010; 86: 427–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

