Protein O-fucosylation: structure and function
- PMID: 30690220
- PMCID: PMC6656592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2018.12.005
Protein O-fucosylation: structure and function
Abstract
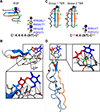
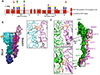
Fucose is a common terminal modification on protein and lipid glycans. Fucose can also be directly linked to protein via an O-linkage to Serine or Threonine residues located within consensus sequences contained in Epidermal Growth Factor-like (EGF) repeats and Thrombospondin Type 1 Repeats (TSRs). In this context, fucose is added exclusively to properly folded EGF repeats and TSRs by Protein O-fucosyltransferases 1 and 2, respectively. In both cases, the O-linked fucose can also be elongated with other sugars. Here, we describe the biological importance of these O-fucose glycans and molecular mechanisms by which they affect the function of the proteins they modify. O-Fucosylation of EGF repeats modulates the Notch signaling pathway, while O-fucosylation of TSRs is predicted to influence secretion of targets including several extracellular proteases. Recent data show O-fucose glycans mediate their effects by participating in both intermolecular and intramolecular interactions.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Swearingen KE, Lindner SE, Shi L, Shears MJ, Harupa A, Hopp CS, Vaughan AM, Springer TA, Moritz RL, Kappe SH, et al. : Interrogating the Plasmodium Sporozoite Surface: Identification of Surface-Exposed Proteins and Demonstration of Glycosylation on CSP and TRAP by Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics. PLoS Pathog 2016, 12:e1005606. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

