Tryptophan carbon dots and their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 30690384
- PMCID: PMC6441370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.031
Tryptophan carbon dots and their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
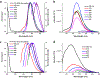
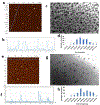
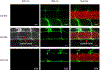
Drug traversal across the blood-brain barrier has come under increasing scrutiny recently, particularly concerning the treatment of sicknesses, such as brain cancer and Alzheimer's disease. Most therapies and medicines are limited due to their inability to cross this barrier, reducing treatment options for maladies affecting the brain. Carbon dots show promise as drug carriers, but they experience the same limitations regarding crossing the blood-brain barrier as many small molecules do. If carbon dots can be prepared from a precursor that can cross the blood-brain barrier, there is a chance that the remaining original precursor molecule can attach to the carbon dot surface and lead the system into the brain. Herein, tryptophan carbon dots were synthesized with the strategy of using tryptophan as an amino acid for crossing the blood-brain barrier via LAT1 transporter-mediated endocytosis. Two types of carbon dots were synthesized using tryptophan and two different nitrogen dopants: urea and 1,2-ethylenediamine. Carbon dots made using these precursors show excitation wavelength-dependent emission, low toxicity, and have been observed inside the central nervous system of zebrafish (Danio rerio). The proposed mechanism for these carbon dots abilities to cross the blood-brain barrier concerns residual tryptophan molecules which attach to the carbon dots surface, enabling them to be recognized by the LAT1 transporter. The role of carbon dots for transport open promising avenues for drug delivery and imaging in the brain.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Carbon dots; Drug delivery; Zebrafish.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crossing the blood-brain-barrier with transferrin conjugated carbon dots: A zebrafish model study.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Sep 1;145:251-256. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.05.007. Epub 2016 May 5. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 27187189
-
Nontoxic amphiphilic carbon dots as promising drug nanocarriers across the blood-brain barrier and inhibitors of β-amyloid.Nanoscale. 2019 Nov 28;11(46):22387-22397. doi: 10.1039/c9nr08194a. Nanoscale. 2019. PMID: 31730144
-
Drug delivery of memantine with carbon dots for Alzheimer's disease: blood-brain barrier penetration and inhibition of tau aggregation.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Jul;617:20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.02.124. Epub 2022 Mar 1. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 35255395 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Carbon Dots for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Dec 23;17:6621-6638. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S388030. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36582459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crossing the blood-brain barrier with nanoparticles.J Control Release. 2018 Jan 28;270:290-303. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.12.015. Epub 2017 Dec 19. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 29269142 Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon Dots: An Innovative Tool for Drug Delivery in Brain Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11783. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111783. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chalcones as Anti-Glioblastoma Stem Cell Agent Alone or as Nanoparticle Formulation Using Carbon Dots as Nanocarrier.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 14;14(7):1465. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071465. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890360 Free PMC article.
-
Troxerutin Delays Skin Keratinocyte Senescence Induced by Ionizing Radiation Both In Vitro and In Vivo.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jan;24(1):e16584. doi: 10.1111/jocd.16584. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39291439 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Food Components as Biocompatible Carriers: A Novel Approach to Glioblastoma Drug Delivery.Foods. 2024 Sep 4;13(17):2812. doi: 10.3390/foods13172812. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39272576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress of emitting long-wavelength carbon dots and their merits for visualization tracking, target delivery and theranostics.Theranostics. 2023 May 21;13(9):3064-3102. doi: 10.7150/thno.80579. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37284447 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu X, Ray R, Gu Y, Ploehn HJ, Gearheart L, Raker K and Scrivens WA, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2004, 126, 12736–12737. - PubMed
-
- Luo PG, Yang F, Yang S-T, Sonkar SK, Yang L, Broglie JJ, Liu Y and Sun Y-P, RSC Adv, 2014, 4, 10791–10807.
-
- Sahu S, Behera B, Maiti TK and Mohapatra S, Chem. Comm, 2012, 48, 8835–8837. - PubMed
-
- Zhu S, Meng Q, Wang L, Zhang J, Song Y, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun H, Wang H and Yang B, Angew. Chem, 2013, 125, 4045–4049. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

