Aquaporin-4 Water Channel in the Brain and Its Implication for Health and Disease
- PMID: 30691235
- PMCID: PMC6406241
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020090
Aquaporin-4 Water Channel in the Brain and Its Implication for Health and Disease
Abstract
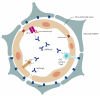
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is a water channel expressed on astrocytic endfeet in the brain. The role of AQP4 has been studied in health and in a range of pathological conditions. Interest in AQP4 has increased since it was discovered to be the target antigen in the inflammatory autoimmune disease neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD). Emerging data suggest that AQP4 may also be implicated in the glymphatic system and may be involved in the clearance of beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this review, we will describe the role of AQP4 in the adult and developing brain as well as its implication for disease.
Keywords: aquaporin-4; autoantibodies; development; disease; glymphatic system; neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nielsen S., Nagelhus E.A., Amiry-Moghaddam M., Bourque C., Agre P., Ottersen O.P. Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: High-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1997;17:171–180. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-01-00171.1997. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa H., Ma T., Skach W., Matthay M.A., Verkman A.S. Molecular cloning of a mercurial-insensitive water channel expressed in selected water-transporting tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:5497–5500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

