In utero exposure to ultrafine particles promotes placental stress-induced programming of renin-angiotensin system-related elements in the offspring results in altered blood pressure in adult mice
- PMID: 30691489
- PMCID: PMC6350404
- DOI: 10.1186/s12989-019-0289-1
In utero exposure to ultrafine particles promotes placental stress-induced programming of renin-angiotensin system-related elements in the offspring results in altered blood pressure in adult mice
Abstract
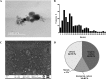
Background: Exposure to particulate matter (PM) is associated with an adverse intrauterine environment, which can promote adult cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. Ultrafine particles (UFP) (small size and large surface area/mass ratio) are systemically distributed, induce inflammation and oxidative stress, and have been associated with vascular endothelial dysfunction and arterial vasoconstriction, increasing hypertension risk. Placental stress and alterations in methylation of promoter regions of renin-angiotensin system (RAS)-related elements could be involved in UFP exposure-related programming of hypertension. We investigated whether in utero UFP exposure promotes placental stress by inflammation and oxidative stress, alterations in hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 11b-type 2 (HSD11B2) and programming of RAS-related elements, and result in altered blood pressure in adult offspring. UFP were collected from ambient air using an aerosol concentrator and physicochemically characterized. Pregnant C57BL/6J pun/pun female mice were exposed to collected UFP (400 μg/kg accumulated dose) by intratracheal instillation and compared to control (nonexposed) and sterile H2O (vehicle) exposed mice. Embryo reabsorption and placental stress by measurement of the uterus, placental and fetal weights, dam serum and fetal cortisol, placental HSD11B2 DNA methylation and protein levels, were evaluated. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) biotransformation (CYP1A1 and NQO1 (NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone)1)) enzymes, inflammation and oxidative stress in placentas and fetuses were measured. Postnatal day (PND) 50 in male offspring blood pressure was measured. Methylation and protein expression of (RAS)-related elements, angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1R) and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) in fetuses and lungs of PND 50 male offspring were also assessed.
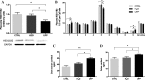
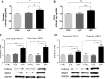
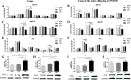
Results: In utero UFP exposure induced placental stress as indicated by an increase in embryo reabsorption, decreases in the uterus, placental, and fetal weights, and HSD11B2 hypermethylation and protein downregulation. In utero UFP exposure induced increases in the PAH-biotransforming enzymes, intrauterine oxidative damage and inflammation and stimulated programming and activation of AT1R and ACE, which resulted in increased blood pressure in the PND 50 male offspring.
Conclusions: In utero UFP exposure promotes placental stress through inflammation and oxidative stress, and programs RAS-related elements that result in altered blood pressure in the offspring. Exposure to UFP during fetal development could influence susceptibility to CVD in adulthood.
Keywords: Hypertension; Placental stress; Programming disease; Ultrafine particles.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Internal Committee for the Use and Care of Laboratory Animals, Cinvestav, in accordance to the “Principles of Laboratory Animal Care” guidelines under protocol No. 0171–15.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
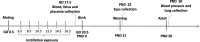
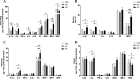
References
-
- Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA, Brook JR, Bhatnagar A, Diez-Roux AV, Holguin F, Hong Y, Luepker RV, Mittleman MA, et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: an update to the scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation. 2010;121:2331–2378. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3181dbece1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

