Roles of the DedD Protein in Escherichia coli Cell Constriction
- PMID: 30692172
- PMCID: PMC6436348
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00698-18
Roles of the DedD Protein in Escherichia coli Cell Constriction
Abstract
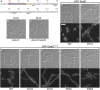
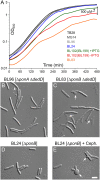
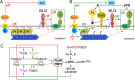
Two key tasks of the bacterial septal-ring (SR) machinery during cell constriction are the generation of an inward-growing annulus of septal peptidoglycan (sPG) and the concomitant splitting of its outer edge into two layers of polar PG that will be inherited by the two new cell ends. FtsN is an essential SR protein that helps trigger the active constriction phase in Escherichia coli by inducing a self-enhancing cycle of processes that includes both sPG synthesis and splitting and that we refer to as the sPG loop. DedD is an SR protein that resembles FtsN in several ways. Both are bitopic inner membrane proteins with small N-terminal cytoplasmic parts and larger periplasmic parts that terminate with a SPOR domain. Though absence of DedD normally causes a mild cell-chaining phenotype, the protein is essential for division and survival of cells with limited FtsN activity. Here, we find that a small N-terminal portion of DedD (NDedD; DedD1-54) is required and sufficient to suppress ΔdedD-associated division phenotypes, and we identify residues within its transmembrane domain that are particularly critical to DedD function. Further analyses indicate that DedD and FtsN act in parallel to promote sPG synthesis, possibly by engaging different parts of the FtsBLQ subcomplex to induce a conformation that permits and/or stimulates the activity of sPG synthase complexes composed of FtsW, FtsI (PBP3), and associated proteins. We propose that, like FtsN, DedD promotes cell fission by stimulating sPG synthesis, as well as by providing positive feedback to the sPG loop.IMPORTANCE Cell division (cytokinesis) is a fundamental biological process that is incompletely understood for any organism. Division of bacterial cells relies on a ring-like machinery called the septal ring or divisome that assembles along the circumference of the mother cell at the site where constriction eventually occurs. In the well-studied bacterium Escherichia coli, this machinery contains over 30 distinct proteins. We identify functionally important parts of one of these proteins, DedD, and present evidence supporting a role for DedD in helping to induce and/or sustain a self-enhancing cycle of processes that are executed by fellow septal-ring proteins and that drive the active constriction phase of the cell division cycle.
Keywords: FtsA; FtsB; FtsL; FtsQ; cell division.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

