Adiposity in relation to risks of fatty liver, cirrhosis and liver cancer: a prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults
- PMID: 30692555
- PMCID: PMC6349919
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36460-7
Adiposity in relation to risks of fatty liver, cirrhosis and liver cancer: a prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults
Abstract
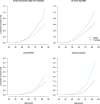
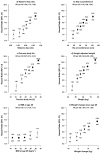
Adiposity is an increasing public health problem in China. We aimed to examine the associations of adiposity with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and other chronic liver diseases in Chinese adults. The prospective China Kadoorie Biobank recruited 512,891 adults aged 30-79 years from 10 areas. During 10 years of follow-up, 7,386 incident liver disease cases were recorded among 503,991 participants without prior cancer or chronic liver disease at baseline. The mean body mass index (BMI) (SD) was 23.7 (3.3) kg/m2 and mean waist circumference (WC) 80.3 (9.8) cm, with 33% having BMI ≥25 kg/m2. Throughout the range examined (BMI 15-50) BMI showed a log-linear positive association with NAFLD (n = 1,298), with adjusted HR per 5 kg/m2 of 2.81 (95% CI 2.63-3.01), adjusting for regression dilution. There were also positive associations of percent body fat, WC, and waist-to-hip ratio with NAFLD, with HRs per 1-SD of 2.27 (2.14-2.41), 2.60 (2.44-2.76), and 1.84 (1.76-1.92). BMI was unrelated to viral hepatitis (n = 1,477), and had a U-shaped association with cirrhosis (n = 2,082) and an inverse association with liver cancer (n = 2,568), which disappeared after excluding the first 5 years of follow-up. Among Chinese adults, adiposity was a major risk factor for NAFLD but not other chronic liver diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

