Bedside ultrasonography for the confirmation of gastric tube placement in the neonate
- PMID: 30692884
- PMCID: PMC6329247
- DOI: 10.4103/sja.SJA_413_18
Bedside ultrasonography for the confirmation of gastric tube placement in the neonate
Abstract
Background: Naso/Orogastric tube (NOGT) misplacement can lead to significant complications. Therefore, the assessment of tube position is essential to ensure patient safety. Although radiography is considered the gold standard for determining NOGT location, new methods may be helpful in reducing repetitive radiation exposure, especially for neonates. In this study, we sought to investigate if bedside ultrasonography (BUSG) can be used to verify NOGT placement in neonatal intensive care patients.
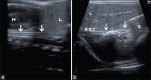
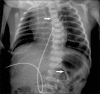
Materials and methods: Infants requiring NOGT placement were enrolled. After insertion of the NOGT, the location was first identified using BUSG and then confirmed using abdominal radiography for comparison.
Results: The study cohort included 51 infants with an average gestational age of 34 ± 4.9 weeks. BUSG determined the NOGT location correctly with a sensitivity of 92.2%. The location of the NOGT could not be determined by BUSG in four neonates (7.8%). In one infant, the NOGT was positioned in the esophagus, as determined both by BUSG and radiography.
Conclusion: BUSG is a promising diagnostic tool for determining NOGT location in neonates, thereby eliminating the need for abdominal radiography.
Keywords: Enteral nutrition; infant; intensive care units; nasogastric tube; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lyman B, Kemper C, Northington L, Yaworski JA, Wilder K, Moore C, et al. Use of temporary enteral access devices in hospitalized neonatal and pediatric patients in the United States. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016;40:574–80. - PubMed
-
- Metheny NA, Meert KL, Clouse RE. Complications related to feeding tube placement. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007;23:178–82. - PubMed
-
- Creel AM, Winkler MK. Oral and nasal enteral tube placement errors and complications in a pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007;8:161–4. - PubMed
-
- Society of Pediatric Nurses (SPN) Clinical Practice Committee, SPN Research Committee. Longo MA. Best evidence: Nasogastric tube placement verification. J Pediatr Nurs. 2011;26:373–6. - PubMed
-
- Irving SY, Lyman B, Northington L, Bartlett JA, Kemper C, et al. NOVEL Project Work Group. Nasogastric tube placement and verification in children: Review of the current literature. Nutr Clin Pract. 2014;29:267–76. - PubMed

