Efficacy of Alvogyl (Combination of Iodoform + Butylparaminobenzoate) and Zinc Oxide Eugenol for Dry Socket
- PMID: 30693231
- PMCID: PMC6327816
- DOI: 10.4103/ams.ams_167_18
Efficacy of Alvogyl (Combination of Iodoform + Butylparaminobenzoate) and Zinc Oxide Eugenol for Dry Socket
Abstract
Context: Alveolar osteitis (AO) (dry socket) is a postoperative healing complication after tooth extraction. Pain is considered the most important symptom of dry socket which can vary in frequency and intensity.
Aim: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the management of AO with alvogyl and zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE).
Study design: This study was designed as a single-blinded prospective study with a sample size of fifty patients included in the study after obtaining the informed consent.
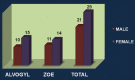
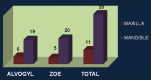
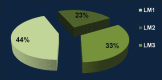
Materials and methods: All the fifty patients with dry socket were randomly selected and divided into two groups as follows: (1) Group I: Patients who received alvogyl paste as an intrasocket medication and (2) Group II: Patients who received ZOE as an obtundant dressing.
Statistical analysis used: Data were analyzed using t-test and Chi-square test.
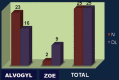
Results: The mean number of dressings required was less in Group I as compared to Group II, and thus Group I showed faster healing. In addition, the intensity of pain decreased more rapidly in Group I as compared to Group II. The mean time required for complete pain relief was less in Group I as compared to Group II, and thus Group I showed faster relief from pain.
Conclusion: Alvogyl is better for the management of dry socket by virtue of shorter time required for complete pain relief, fewer visits for dressing change, and faster clinical healing of the socket.
Keywords: Alveolar osteitis; alvogyl; dry socket; zinc oxide eugenol.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Blum IR. Contemporary views on dry socket (alveolar osteitis): A clinical appraisal of standardization, aetiopathogenesis and management: A critical review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;31:309–17. - PubMed
-
- Alwraikat AA. Alveolar osteitis: Incidence and risk factors following third molar surgery in Jordan. Pak Oral Dent J. 2009;29:19–22.
-
- Sheikh MA, Kiyani A, Mehdi A, Musharaf Q. Pathogenesis and management of dry socket (alveolar osteitis) Pak Oral Dent J. 2010;30:323–6.
-
- Preetha S. An overview of dry socket and its management. J Dent Med Sci May. 2014;13:32–5.
-
- Torres-Lagares D, Infante-Cossio P, Gutierrez-Perez JL, Romero-Ruiz MM, Garcia-Calderon M, Serrera-Figallo MA, et al. Intra-alveolar chlorhexidine gel for the prevention of dry socket in mandibular third molar surgery. A pilot study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006;11:E179–84. - PubMed

