Cervicofacial Actinomycosis and its Management
- PMID: 30693266
- PMCID: PMC6327805
- DOI: 10.4103/ams.ams_176_18
Cervicofacial Actinomycosis and its Management
Abstract
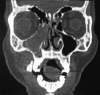
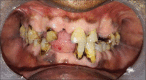
Cervicofacial actinomycosis is an invasive destructive infectious syndrome, caused by Gram-positive, branching filamentous bacteria, Actinomyces. Most of the cases are traced to an odontogenic source with periapical abscess and posttraumatic or surgical complications with poor hygiene and immunosuppression as contributing factors. Diagnosis is often delayed because of nonspecific and prolonged symptoms usually mimicking a malignant or a granulomatous lesion. Solitary or multiple abscesses and fistula formation across normal tissue planes accompany chronic draining lesions and may lead to invasion of viscera. Hence, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment is mandatory to reduce morbidity. In this paper, we report two cases of cervicofacial actinomycosis, one presented with intraoral granulomatous lesion treated with surgical curettage and intramuscular penicillin and another case with extraoral swelling and multiple draining sinuses treated with oral antibiotics.
Keywords: Actinomycosis; cervicofacial; granulomatous.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Belmont MJ, Behar PM, Wax MK. Atypical presentations of actinomycosis. Head Neck. 1999;21:264–8. - PubMed
-
- Pradhan S, Datta NR, Prasad KN, Ayyagari S, Pandey R. Actinomycosis mimicking carcinoma of the maxillary sinus. Indian J Cancer. 1993;30:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Lerner PI. The lumpy jaw. Cervicofacial actinomycosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1988;2:203–20. - PubMed
-
- Bochev V, Angelova I, Tsankov N. Cervicofacial actinomycosis – Report of two cases. Acta Dermatovenerol APA. 2003;12:105–8.
-
- Vorasubin N, Wu AW, Day C, Suh JD. Invasive sinonasal actinomycosis: Case report and literature review. Laryngoscope. 2013;123:334–8. - PubMed

