Retained Solitaire FR device after mechanical thrombectomy: Case review and management strategies
- PMID: 30693345
- PMCID: PMC6329211
- DOI: 10.4103/bc.bc_12_18
Retained Solitaire FR device after mechanical thrombectomy: Case review and management strategies
Abstract
Solitaire FR device is a Food and Drug Administration-approved device for mechanical thrombectomy. It has been tested in various clinical trials for its safety and efficacy. We report a case of inadvertent detachment of the Solitaire FR device at stent-stent wire interface while performing mechanical thrombectomy. We review a rare phenomenon of retained Solitaire FR stent retriever in situ and discuss technique of avoidance and its management.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Solitaire; retained device; thrombectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
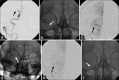
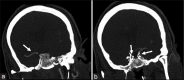
References
-
- Nogueira RG, Levy EI, Gounis M, Siddiqui AH. The Trevo device: Preclinical data of a novel stroke thrombectomy device in two different animal models of arterial thrombo-occlusive disease. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012;4:295–300. - PubMed
-
- Grech R, Pullicino R, Thornton J, Downer J. An efficacy and safety comparison between different Stentriever designs in acute ischaemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Radiol. 2016;71:48–57. - PubMed

