Milk Thistle Treatment for Children and Adults with Trichotillomania: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Negative Study
- PMID: 30694881
- PMCID: PMC6420084
- DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001005
Milk Thistle Treatment for Children and Adults with Trichotillomania: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Negative Study
Abstract
Background: Data on the pharmacological treatment of trichotillomania are limited. Milk thistle has antioxidant properties and showed promise in trichotillomania in a prior case report. The goal of the current study was to determine the efficacy and tolerability of silymarin in children and adults with trichotillomania.
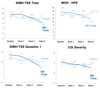
Methods: Twenty individuals (19 [95.0%] women; 16 adults; mean age, 27.9 [11.5] years) with trichotillomania entered a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study (6 weeks of milk thistle and 6 weeks of placebo with a 1-week wash-out in between). Dosing of milk thistle ranged from 150 mg twice a day to 300 mg twice a day. Subjects were assessed with the National Institute of Mental Health Trichotillomania Severity Scale (primary outcome), the Massachusetts General Hospital Hair Pulling Scale, Clinical Global Impression scale, and measures of depression, anxiety, and psychosocial functioning. Outcomes were examined using linear mixed models with a random intercept for subject and t tests.
Results: There were no statistically significant treatment type-by-time interactions for the main outcome measure, but significant effects were seen for secondary measures (eg, time spent pulling per day for the past week). From baseline to week 6, there was a significant decrease in Clinical Global Impression severity for the milk thistle group but not in the placebo group.
Conclusions: This trial failed to show that milk thistle was more effective than placebo on the main outcome measure, but milk thistle did demonstrate significant improvements on select secondary outcome measures. These findings may shed light on important neurochemical targets worthy of future investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosure information: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Diefenbach GJ, Tolin DF, Hannan S, et al. Trichotillomania: impact on psychosocial functioning and quality of life. Behav Res Ther. 2005;43:869–884. - PubMed
-
- Odlaug BL, Kim SW, Grant JE. Quality of life and clinical severity in pathological skin picking and trichotillomania. J Anxiety Disord. 2010;24:823–829. - PubMed
-
- Grant JE, Odlaug BL, Kim SW. N-acetylcysteine, a glutamate modulator, in the treatment of trichotillomania: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66:756–763. - PubMed
-
- Van Ameringen M, Mancini C, Patterson B, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of olanzapine in the treatment of trichotillomania. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71:1336–1343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous