Real-Time Interferometric Refractive Index Change Measurement for the Direct Detection of Enzymatic Reactions and the Determination of Enzyme Kinetics
- PMID: 30696020
- PMCID: PMC6387378
- DOI: 10.3390/s19030539
Real-Time Interferometric Refractive Index Change Measurement for the Direct Detection of Enzymatic Reactions and the Determination of Enzyme Kinetics
Abstract
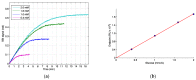
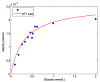
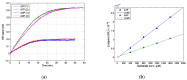
Back scatter interferometry (BSI) is a sensitive method for detecting changes in the bulk refractive index of a solution in a microfluidic system. Here we demonstrate that BSI can be used to directly detect enzymatic reactions and, for the first time, derive kinetic parameters. While many methods in biomedical assays rely on detectable biproducts to produce a signal, direct detection is possible if the substrate or the product exert distinct differences in their specific refractive index so that the total refractive index changes during the enzymatic reaction. In this study, both the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, catalyzed by hexokinase, and the conversion of adenosine-triphosphate to adenosine di-phosphate and mono-phosphate, catalyzed by apyrase, were monitored by BSI. When adding hexokinase to glucose solutions containing adenosine-triphosphate, the conversion can be directly followed by BSI, which shows the increasing refractive index and a final plateau corresponding to the particular concentration. From the initial reaction velocities, KM was found to be 0.33 mM using Michaelis⁻Menten kinetics. The experiments with apyrase indicate that the refractive index also depends on the presence of various ions that must be taken into account when using this technique. This study clearly demonstrates that measuring changes in the refractive index can be used for the direct determination of substrate concentrations and enzyme kinetics.
Keywords: dn/dc; enzyme; interferometry; refractive index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sun J., Chan C.C., Zhang Y.F., Zheng L.T., Ho H.L., Dong X.Y., Shao L.Y. Glucose optical biosensor with sol-gel-coated long-period gratings. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics. 2008;7134:713443. doi: 10.1117/12.803263. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

