Cognitive and motor outcomes in children born low birth weight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies from South Asia
- PMID: 30696415
- PMCID: PMC6350290
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-019-1408-8
Cognitive and motor outcomes in children born low birth weight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies from South Asia
Abstract
Background: South Asia contributes substantially to global low birth weight population (i.e. those with birth weight < 2500 g). Synthesized evidence is lacking on magnitude of cognitive and motor deficits in low birth weight (LBW) children compared to those with normal birth weight (NBW) (i.e. birth weight ≥ 2500 g). The meta-analysis aimed to generate this essential evidence.
Methods: Literature search was performed using PubMed and Google Scholar. Original research articles from south Asia that compared cognitive and/or motor scores among LBW and NBW individuals were included. Weighted mean differences (WMD) and pooled relative risks (RR) were calculated. All analyses were done using STATA 14 software.
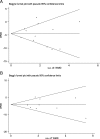
Results: Nineteen articles (n = 5999) were included in the analysis. Children < 10 years of age born LBW had lower cognitive (WMD -4.56; 95% CI: -6.38, - 2.74) and motor scores (WMD -4.16; 95% CI: -5.42, - 2.89) compared to children with NBW. Within LBW children, those with birth weight < 2000 g had much lower cognitive (WMD -7.23, 95% CI; - 9.20, - 5.26) and motor scores (WMD -6.45, 95% CI; - 9.64, - 3.27).
Conclusions: In south Asia, children born LBW, especially with < 2000 g birth weight, have substantial cognitive and motor impairment compared to children with NBW. Early child development interventions should lay emphasis to children born LBW.
Keywords: Adolescents; Children; Cognitive score; Low birth weight; Motor score; South Asia.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- World Bank country and lending groups. Available at: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-b.... Accessed 26 Nov 2018.
-
- Lee AC, Katz J, Blencowe H, Kozuki N, Vogel JP, Adair L, et al. National and regional estimates of term and preterm babies born small for gestational age in 138 low-income and middle-income countries in 2010. Lancet Glob Health. 2013;1(1):e26–e36. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70006-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- United Nations Children’s Fund and World Health Organization. Low Birth weight: Country, regional and global estimates. New York: UNICEF; 2004. https://www.unicef.org/publications/files/low_birthweight_from_EY.pdf. Accessed 28 Nov 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

