Review of the impact of MALDI-TOF MS in public health and hospital hygiene, 2018
- PMID: 30696525
- PMCID: PMC6351997
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.4.1800193
Review of the impact of MALDI-TOF MS in public health and hospital hygiene, 2018
Abstract
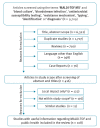
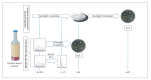
IntroductionMALDI-TOF MS represents a new technological era for microbiology laboratories. Improved sample processing and expanded databases have facilitated rapid and direct identification of microorganisms from some clinical samples. Automated analysis of protein spectra from different microbial populations is emerging as a potential tool for epidemiological studies and is expected to impact public health.AimTo demonstrate how implementation of MALDI-TOF MS has changed the way microorganisms are identified, how its applications keep increasing and its impact on public health and hospital hygiene.MethodsA review of the available literature in PubMED, published between 2009 and 2018, was carried out.ResultsOf 9,709 articles retrieved, 108 were included in the review. They show that rapid identification of a growing number of microorganisms using MALDI-TOF MS has allowed for optimisation of patient management through prompt initiation of directed antimicrobial treatment. The diagnosis of Gram-negative bacteraemia directly from blood culture pellets has positively impacted antibiotic streamlining, length of hospital stay and costs per patient. The flexibility of MALDI-TOF MS has encouraged new forms of use, such as detecting antibiotic resistance mechanisms (e.g. carbapenemases), which provides valuable information in a reduced turnaround time. MALDI-TOF MS has also been successfully applied to bacterial typing.ConclusionsMALDI-TOF MS is a powerful method for protein analysis. The increase in speed of pathogen detection enables improvement of antimicrobial therapy, infection prevention and control measures leading to positive impact on public health. For antibiotic susceptibility testing and bacterial typing, it represents a rapid alternative to time-consuming conventional techniques.
Keywords: MALDI-TOF MS; Mass Spectrometry; antibiotic resistance mechanisms; antibiotic use; hygiene; microorganism identification; mycobacteria; typing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lévesque S, Dufresne PJ, Soualhine H, Domingo MC, Bekal S, Lefebvre B, et al. A Side by Side Comparison of Bruker Biotyper and VITEK MS: Utility of MALDI-TOF MS Technology for Microorganism Identification in a Public Health Reference Laboratory. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144878. 10.1371/journal.pone.0144878 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spanu T, Posteraro B, Fiori B, D’Inzeo T, Campoli S, Ruggeri A, et al. Direct maldi-tof mass spectrometry assay of blood culture broths for rapid identification of Candida species causing bloodstream infections: an observational study in two large microbiology laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50(1):176-9. 10.1128/JCM.05742-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martiny D, Debaugnies F, Gateff D, Gérard M, Aoun M, Martin C, et al. Impact of rapid microbial identification directly from positive blood cultures using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry on patient management. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013;19(12):E568-81. 10.1111/1469-0691.12282 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clerc O, Prod’hom G, Vogne C, Bizzini A, Calandra T, Greub G. Impact of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry on the clinical management of patients with Gram-negative bacteremia: a prospective observational study. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(8):1101-7. 10.1093/cid/cis1204 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources