Fine mapping of a major quantitative trait locus, qgnp7(t), controlling grain number per panicle in African rice (Oryza glaberrima S.)
- PMID: 30697122
- PMCID: PMC6345233
- DOI: 10.1270/jsbbs.18084
Fine mapping of a major quantitative trait locus, qgnp7(t), controlling grain number per panicle in African rice (Oryza glaberrima S.)
Abstract
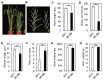
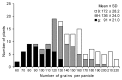
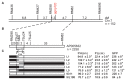
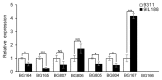
Grain number per panicle is a major component of rice yield that is typically controlled by many quantitative trait loci (QTLs). The identification of genes controlling grain number per panicle in rice would be valuable for the breeding of high-yielding rice. The Oryza glaberrima chromosome segment substitution line 9IL188 had significantly smaller panicles compared with the recurrent parent 9311. QTL analysis in an F2 population derived from a cross between 9IL188 and 9311 revealed that qgnp7(t), a major QTL located on the short arm of chromosome 7, was responsible for this phenotypic variation. Fine mapping was conducted using a large F3 population containing 2250 individuals that were derived from the F2 heterozygous plants. Additionally, plant height, panicle length, and grain number per panicle of the key F4 recombinant families were examined. Through two-step substitution mapping, qgnp7(t) was finally localized to a 41 kb interval in which eight annotated genes were identified according to available sequence annotation databases. Phenotypic evaluation of near isogenic lines (NIL-qgnp7 and NIL-qGNP7) indicated that qgnp7(t) has pleiotropic effects on rice plant architecture and panicle structure. In addition, yield estimation of NILs indicated that qGNP7(t) derived from 9311 is the favorable allele. Our results provide a foundation for isolating qgnp7(t). Markers flanking this QTL will be a useful tool for the marker-assisted selection of favorable alleles in O. glaberrima improvement programs.
Keywords: African rice (Oryza glaberrima S.); chromosome segment substituted lines; fine mapping; grain number per panicle.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus for grain number per panicle from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.).Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Aug;113(4):619-29. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0326-y. Epub 2006 Jun 13. Theor Appl Genet. 2006. PMID: 16770601
-
Fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus for spikelet number per panicle in a new plant type rice and evaluation of a near-isogenic line for grain productivity.J Exp Bot. 2017 May 17;68(11):2693-2702. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx128. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 28582550 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association analysis identifies natural allelic variants associated with panicle architecture variation in African rice, Oryza glaberrima Steud.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Sep 30;13(10):jkad174. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad174. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 37535690 Free PMC article.
-
Yield-related QTLs and their applications in rice genetic improvement.J Integr Plant Biol. 2012 May;54(5):300-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2012.01117.x. J Integr Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22463712 Review.
-
Marker-assisted selection for grain number and yield-related traits of rice (Oryza sativa L.).Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020 May;26(5):885-898. doi: 10.1007/s12298-020-00773-7. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020. PMID: 32377039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Selection of Gamma-Ray Irradiated Higher Yield Rice Mutants by Directed Evolution Method.Plants (Basel). 2020 Aug 7;9(8):1004. doi: 10.3390/plants9081004. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32784591 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Analysis of BSA-Seq Based Mapping, RNA-Seq, and Metabolomic Unraveled Candidate Genes Associated with Panicle Grain Number in Rice (Oryza sativa L.).Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 29;12(7):918. doi: 10.3390/biom12070918. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883474 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, pyramid, and candidate gene of QTL for yield-related traits based on rice CSSLs in indica Xihui18 background.Mol Breed. 2022 Mar 24;42(4):19. doi: 10.1007/s11032-022-01284-x. eCollection 2022 Apr. Mol Breed. 2022. PMID: 37309460 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-quantitative trait loci analysis identified consensus genomic regions and candidate genes associated with grain yield in rice.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 16;13:1035851. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1035851. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36466247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashikari, M., Sakakibara, H., Lin, S., Yamamoto, T., Takashi, T., Nishimura, A., Angeles, E.R., Qian, Q., Kitano, H. and Matsuoka, M. (2005) Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science 309: 741–745. - PubMed
-
- Deshmukh, R., Singh, A., Jain, N., Anand, S., Gacche, R., Singh, A., Gaikwad, K., Sharma, T., Mohapatra, T. and Singh, N. (2010) Identification of candidate genes for grain number in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Funct. Integr. Genomics 10: 339–347. - PubMed
-
- Howell, P.M., Lydiate, D.J. and Marshall, D.F. (1996) Towards developing intervarietal substitution lines in Brassica napus using marker-assisted selection. Genome 39: 348–358. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
