Mechanisms of Pancreatic Injury Induced by Basic Amino Acids Differ Between L-Arginine, L-Ornithine, and L-Histidine
- PMID: 30697165
- PMCID: PMC6341295
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01922
Mechanisms of Pancreatic Injury Induced by Basic Amino Acids Differ Between L-Arginine, L-Ornithine, and L-Histidine
Abstract
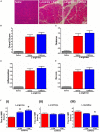
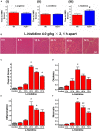
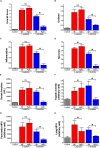
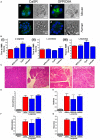
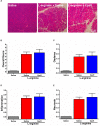
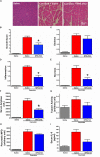
Pancreatic acinar cells require high rates of amino acid uptake for digestive enzyme synthesis, but excessive concentrations can trigger acute pancreatitis (AP) by mechanisms that are not well understood. We have used three basic natural amino acids L-arginine, L-ornithine, and L-histidine to determine mechanisms of amino acid-induced pancreatic injury and whether these are common to all three amino acids. Caffeine markedly inhibited necrotic cell death pathway activation in isolated pancreatic acinar cells induced by L-arginine, but not L-ornithine, whereas caffeine accelerated L-histidine-induced cell death. Both necroptosis inhibitors of RIPK1 and RIPK3 and a necroptosis activator/apoptosis inhibitor z-VAD increased cell death caused by L-histidine, but not L-arginine or L-ornithine. Cyclophilin D knock-out (Ppif-/-) significantly attenuated cell death induced by L-histidine, but not L-arginine, or L-ornithine. Allosteric modulators of calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) and G-protein coupled receptor class C group 6 member A (GPRC6A) had inhibitory effects on cell death induced by L-arginine but not L-ornithine or L-histidine. We developed a novel amino acid-induced AP murine model with high doses of L-histidine and confirmed AP severity was significantly reduced in Ppif-/- vs. wild type mice. In L-arginine-induced AP neither Ppif-/-, caffeine, or allosteric modulators of CaSR or GPRC6A reduced pancreatic damage, even though CaSR inhibition with NPS-2143 significantly reduced pancreatic and systemic injury in caerulein-induced AP. These findings demonstrate marked differences in the mechanisms of pancreatic injury induced by different basic amino acids and suggest the lack of effect of treatments on L-arginine-induced AP may be due to conversion to L-ornithine in the urea cycle.
Keywords: G-protein coupled receptors class C; acute pancreatitis; amino acids; caffeine; cyclophilin D; mitochondria; necroptosis.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong J. A., Cash N. J., Ouyang Y., Morton J. C., Chvanov M., Latawiec D., et al. (2018). Oxidative stress alters mitochondrial bioenergetics and modifies pancreatic cell death independently of cyclophilin D, resulting in an apoptosis-to-necrosis shift. J. Biol. Chem. 293 8032–8047. 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

