What is a balanced knee replacement?
- PMID: 30697441
- PMCID: PMC6335603
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.3.180008
What is a balanced knee replacement?
Abstract
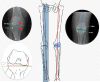
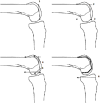
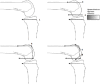
For multifactorial reasons an estimated 20% of patients remain unsatisfied after total knee arthroplasty (TKA).Appropriate tension of the soft tissue envelope encompassing the knee is important in total knee arthroplasty and soft tissue imbalance contributes to several of the foremost reasons for revision TKA, including instability, stiffness and aseptic loosening.There is debate in the literature surrounding the optimum way to achieve balancing of a total knee arthroplasty and there is also a lack of an accepted definition of what a balanced knee replacement is.It may be intuitive to use the native knee as a model for balancing; however, there are many difficulties with translating this into a successful prosthesis.One of the foundations of TKA, as described by Insall, was that although the native knee has more weight transmitted through the medial compartment this was to be avoided in a TKA as it would lead to uneven wear and early failure. There is a focus on achieving symmetrical tension and pressure and subsequent 'balance' in TKA, but the evidence from cadaveric studies is that the native knee is not symmetrically balanced.As we are currently trying to design an implant that is not based on its anatomical counterpart, is it possible to create a truly balanced prosthesis or to even to define what that balance is? The authors have reviewed the current evidence surrounding TKA balancing and its relationship with the native knee. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2018;3:614-619. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.3.180008.
Keywords: measured resection; patient outcomes; soft tissue balancing; total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Sheth NP, Husain A, Nelson CL. Surgical techniques for total knee arthroplasty: measured resection, gap balancing, and hybrid. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2017;25:499–508. - PubMed
-
- Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD. Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2009;24:560–569. - PubMed
-
- Verstraete MA, Meere PA, Salvadore G, Victor J, Walker PS. Contact forces in the tibiofemoral joint from soft tissue tensions: implications to soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. J Biomech 2017;58:195-202. - PubMed
-
- Gustke KA, Golladay GJ, Roche MW, Elson LC, Anderson CR. A targeted approach to ligament balancing using kinetic sensors. J Arthroplasty 2017;32(7):2127-2132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

