Advances in biology of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 30697448
- PMCID: PMC6334189
Advances in biology of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and therapeutic implications
Abstract
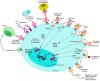
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common pediatric cancer and also occurs in adults. Although the outcomes of multi-agent chemotherapy regimens have greatly improved, high toxicity and relapses in many patients necessitate the development of novel therapeutic approaches. Advances in molecular profiling and cytogenetics have identified a broad range of genetic abnormalities, including gene mutations, chromosome translocations and aneuploidy, which has provided a more comprehensive understanding of the biology and pathogenesis of ALL. This understanding has also led to new targeted therapeutic approaches, including the use of selective small molecule inhibitors, nucleic acid-based therapies and immune-based therapies mediated by specific monoclonal antibodies and cellular immunotherapy, which are poised to revolutionize the treatment of various ALL subtypes. The main focus of this review is to highlight the latest advances in ALL biology, including the identification of prognostic factors and putative therapeutic targets. We also review the current status of, and ongoing progress in, the development of targeted therapies for ALL.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; cytogenetics; immunotherapy; leukemia; molecular subtypes; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Hunger SP, Mullighan CG. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1541–52. - PubMed
-
- Santiago R, Vairy S, Sinnett D, Krajinovic M, Bittencourt H. Novel therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017;18:1081–99. - PubMed
-
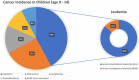
- Linabery AM, Ross JA. Trends in childhood cancer incidence in the U.S. (1992-2004) Cancer. 2008;112:416–32. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
