Prolonged Exposure to Insulin Inactivates Akt and Erk1/2 and Increases Pancreatic Islet and INS1E β-Cell Apoptosis
- PMID: 30697602
- PMCID: PMC6344346
- DOI: 10.1210/js.2018-00140
Prolonged Exposure to Insulin Inactivates Akt and Erk1/2 and Increases Pancreatic Islet and INS1E β-Cell Apoptosis
Abstract
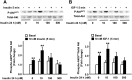
Chronic hyperinsulinemia, in vivo, increases the resistance of peripheral tissues to insulin by desensitizing insulin signaling. Insulin, in a heterologous manner, can also cause IGF-1 resistance. The aim of the current study was to investigate whether insulin-mediated insulin and IGF-1 resistance develops in pancreatic β-cells and whether this resistance results in β-cell decompensation. Chronic exposure of rat islets or INS1E β-cells to increasing concentrations of insulin decreased AktS473 phosphorylation in response to subsequent acute stimulation with 10 nM insulin or IGF-1. Prolonged exposure to high insulin levels not only inhibited AktS473 phosphorylation, but it also resulted in a significant inhibition of the phosphorylation of P70S6 kinase and Erk1/2 phosphorylation in response to the acute stimulation by glucose, insulin, or IGF-1. Decreased activation of Akt, P70S6K, and Erk1/2 was associated with decreased insulin receptor substrate 2 tyrosine phosphorylation and insulin receptor β-subunit abundance; neither IGF receptor β-subunit content nor its phosphorylation were affected. These signaling impairments were associated with decreased SERCA2 expression, perturbed plasma membrane calcium current and intracellular calcium handling, increased endoplasmic reticulum stress markers such as eIF2α S51 phosphorylation and Bip (GRP78) expression, and increased islet and β-cell apoptosis. We demonstrate that prolonged exposure to high insulin levels induces not only insulin resistance, but in a heterologous manner causes resistance to IGF-1 in rat islets and insulinoma cells resulting in decreased cell survival. These findings suggest the possibility that chronic exposure to hyperinsulinemia may negatively affect β-cell mass by increasing β-cell apoptosis.
Keywords: ER-stress; hyperinsulinemia; insulin/IGF-1 signaling; islet and β-cell apoptosis.
Figures








References
-
- Chiasson JL, Rabasa-Lhoret R. Prevention of type 2 diabetes: insulin resistance and beta-cell function. Diabetes. 2004;53(Suppl 3):S34–S38. - PubMed
-
- Shanik MH, Xu Y, Skrha J, Dankner R, Zick Y, Roth J. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: is hyperinsulinemia the cart or the horse? Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl 2):S262–S268. - PubMed
-
- Otani K, Kulkarni RN, Baldwin AC, Krutzfeldt J, Ueki K, Stoffel M, Kahn CR, Polonsky KS. Reduced β-cell mass and altered glucose sensing impair insulin-secretory function in βIRKO mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286(1):E41–E49. - PubMed
-
- Kulkarni RN, Holzenberger M, Shih DQ, Ozcan U, Stoffel M, Magnuson MA, Kahn CR. β-Cell-specific deletion of the Igf1 receptor leads to hyperinsulinemia and glucose intolerance but does not alter β-cell mass. Nat Genet. 2002;31(1):111–115. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
