Sentinel node navigation surgery in esophageal cancer
- PMID: 30697605
- PMCID: PMC6345658
- DOI: 10.1002/ags3.12206
Sentinel node navigation surgery in esophageal cancer
Abstract
Over the last 20 years, the sentinel node (SN) concept has been widely applied to the surgical staging of both breast cancer and melanoma. However, the validity of this concept has been controversial for esophageal cancer, because SN mapping for esophageal cancer is not considered to be technically easy because of the complicated multidirectional lymphatic networks of the esophagus and mediastinum. Nevertheless, studies including meta-analyses indicated that SN mapping may be feasible in early esophageal cancer. Transthoracic esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy was developed as a potential curative procedure for thoracic esophageal cancer. However, this highly invasive procedure might increase morbidity and reduce patients' quality of life (QOL) after esophagectomy. Although further validation based on multicenter trials using the standard protocol of SN mapping for esophageal cancer is required, SN navigation surgery would enable us to carry out personalized and limited lymph node dissection which might reduce morbidity and maintain patients' QOL.
Keywords: esophageal cancer; micrometastasis; radioisotope; sentinel node.
Figures

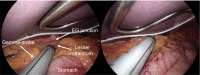
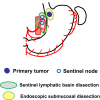
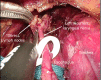
References
-
- Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381:400–12. - PubMed
-
- Lordick F, Mariette C, Haustermans K, Obermannová R, Arnold D; ESMO Guidelines Committee . Oesophageal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(Suppl 5):v50–7. - PubMed
-
- Fujita H, Kakegawa T, Yamana H, et al. Mortality and morbidity rates, postoperative course, quality of life, and prognosis after extended radical lymphadenectomy for esophageal cancer. Comparison of three‐field lymphadenectomy with two‐field lymphadenectomy. Ann Surg. 1995;222:654–62. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

