Health Care Resource Utilization and Exacerbation Rates in Patients with COPD Stratified by Disease Severity in a Commercially Insured Population
- PMID: 30698096
- PMCID: PMC10397829
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2019.25.2.205
Health Care Resource Utilization and Exacerbation Rates in Patients with COPD Stratified by Disease Severity in a Commercially Insured Population
Abstract
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality and is associated with substantial economic burden. There is a lack of data regarding COPD outcomes and costs in a real-world setting, particularly by Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) severity.
Objectives: To (a) characterize a commercially insured U.S. population with COPD and (b) assess prevalence of exacerbations, health care resource utilization (HCRU), costs, and treatment patterns in a cohort of patients with confirmed COPD, overall and stratified by GOLD stage.
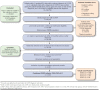
Methods: This retrospective observational cohort study used administrative claims data from the HealthCore Integrated Research Database to identify patients with ≥ 1 inpatient, emergency room (ER), or office visit claim for COPD between January 1, 2012, and November 30, 2013, and continuous enrollment for 1 year before and 2 years after the first COPD diagnosis date. Patients with a spirometry claim within 12 months were eligible for medical record abstraction to confirm COPD diagnosis (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1]/forced vital capacity ratio < 0.7) and GOLD 1-4 classification (based on postbronchodilator FEV1 percent predicted). HCRU, costs, treatment patterns, and rate of moderate/severe exacerbation were identified from diagnosis up to 24 months. Outcomes were analyzed by univariate analysis stratified by GOLD classification. Multivariable analysis was conducted to assess associations between GOLD classification and outcomes of interest.
Results: 53,484 patients newly diagnosed with COPD were identified who met initial inclusion criteria: 14,293 (27%) had a qualifying spirometry claim, and 1,505 had confirmed COPD (GOLD 1, 333 [22%]; GOLD 2, 823 [55%]; GOLD 3, 317 [21%]; GOLD 4, 32 [2%]). Patients with greater disease severity had higher rates of moderate/severe COPD exacerbations (GOLD 1 and 2, 40.4 and 48.9 per 100 person-years, respectively; GOLD 3 and 4, 83.6 and 89.1 per 100 person-years, respectively). All-cause and COPD-related inpatient admissions, COPD-related office visits, and COPD-related ER visits were more prevalent with more severe GOLD classification. Mean annual COPD-related medical costs increased with GOLD classification ($5,945 for GOLD 1 patients, $18,070 for GOLD 4). COPD maintenance medication was filled by 42%, 56%, 73%, and 75% of patients in GOLD 1-4 (57% overall), respectively; combination corticosteroid/long-acting beta2-agonist inhalers were the most commonly used medication, regardless of GOLD classification. Patients with more severe disease had greater adherence (range 44%-68% of days covered for GOLD 1-4) and persistence (range 107-209 days for GOLD 1-4).
Conclusions: Trends toward increases in exacerbations, HCRU, and costs were observed as airflow limitation worsened. Adherence and persistence with COPD maintenance therapy was suboptimal even with severe disease.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals (Ridgefield, CT), which was given the opportunity to review the manuscript for medical and scientific accuracy, as well as intellectual property considerations. Willey and Singer are employees of HealthCore (parent company Anthem), which received funding from Boehringer Ingelheim to complete this study. Wallace and Shinde were employed by HealthCore at the time of this study. Wallace and Singer report stock ownership in Anthem. Napier is an employee of Anthem. Kaila, Bayer, and Shaikh are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticsls. Portions of this research were presented at the following conferences: (a) A. Wallace, S. Kaila, V. Zubek, A. Shaikh, M. Shinde, V. Willey, M. Napier, and J. Singer, Healthcare resource utilization, costs, and exacerbation rates in patients with COPD stratified by GOLD airflow limitation classification in a US commercially insured population, presented at AMCP Nexus 2017; October 16-19, 2017; Dallas, TX; and (b) A.E. Wallace, V. Zubek, S. Kaila, A. Shaikh, M. Shinde, V. Willey, M.B. Napier, and J.R. Singer, Real-world treatment patterns among newly diagnosed COPD patients according to GOLD airflow limitation severity classification in a U.S. commercially insured/Medicare Advantage population, presented at CHEST 2017 Annual Meeting; October 28-November 1, 2017; Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals (Ridgefield, CT), which was given the opportunity to review the manuscript for medical and scientific accuracy, as well as intellectual property considerations. Willey and Singer are employees of HealthCore (parent company Anthem), which received funding from Boehringer Ingelheim to complete this study. Wallace and Shinde were employed by HealthCore at the time of this study. Wallace and Singer report stock ownership in Anthem. Napier is an employee of Anthem. Kaila, Bayer, and Shaikh are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticsls.
Portions of this research were presented at the following conferences: (a) A. Wallace, S. Kaila, V. Zubek, A. Shaikh, M. Shinde, V. Willey, M. Napier, and J. Singer, Healthcare resource utilization, costs, and exacerbation rates in patients with COPD stratified by GOLD airflow limitation classification in a US commercially insured population, presented at AMCP Nexus 2017; October 16-19, 2017; Dallas, TX; and (b) A.E. Wallace, V. Zubek, S. Kaila, A. Shaikh, M. Shinde, V. Willey, M.B. Napier, and J.R. Singer, Real-world treatment patterns among newly diagnosed COPD patients according to GOLD airflow limitation severity classification in a U.S. commercially insured/Medicare Advantage population, presented at CHEST 2017 Annual Meeting; October 28-November 1, 2017; Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Fact sheet. November, 2016. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs315/en/. Accessed December 14, 2018.
-
- D’Souza AO, Shah M, Dhamane AD, Dalal AA. Clinical and economic burden of COPD in a Medicaid population. COPD. 2014;11(2):212-20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous