The Effect of Statins on Levels of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30698163
- PMCID: PMC6348753
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.914128
The Effect of Statins on Levels of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
<strong>BACKGROUND</strong> Currently, statins are used to treat polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to investigate the effect of statins on serum or plasma levels of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in women with PCOS. <strong>MATERIAL AND METHODS</strong> Databases that were searched included PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library from their inception to August of 2018. Published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were identified that evaluated the impact of statins on plasma DHEA levels in women with PCOS. The Cochrane risk of bias tool was used to assess the quality of the included RCTs. A random-effects model was used to analyze the pooled results. <strong>RESULTS</strong> Meta-analysis was performed on data from ten published studies that included 735 patients and showed that statin treatment could significantly reduce plasma DHEA levels when compared with controls (SMD, -0.43; 95% CI, -0.81-0.06; p=0.02; I²=82%). Statins were significantly more effective than placebo in reducing the levels of DHEAs. Subgroup analysis based on statin type showed that atorvastatin significantly reduced DHEA levels (SMD, -0.63; 95% CI, -1.20 - -0.05; p=0.03; I²=38%) but simvastatin did not significantly reduce DHEA levels (SMD: -0.14; 95% CI, -0.49-0.28; p=0.43; I²=77%). Subgroup analysis based on duration of treatment showed no significant difference between 12 weeks of statin treatment (SMD, -0.61; 95% CI, -1.23-0.02; p=0.06; I²=85%) and 24 weeks (SMD, -0.34; 95% CI -0.95-0.28; p=0.29; I²=83%). <strong>CONCLUSIONS</strong> Meta-analysis showed that statins significantly reduced the levels of DHEA when compared with placebo in patients with PCOS.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
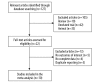
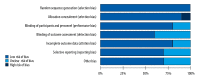



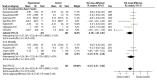
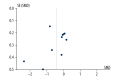
Similar articles
-
The effects of statins on hyperandrogenism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Dec 20;19(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00863-5. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34930305 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of atorvastatin on testosterone levels.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 22;1(1):CD013211. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013211.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33482034 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation into the therapeutic effects of statins with metformin on polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BMJ Open. 2015 Mar 27;5(3):e007280. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007280. BMJ Open. 2015. PMID: 25818277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy of statins, metformin, spironolactone and combined oral contraceptives in reducing testosterone levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.BMC Womens Health. 2020 Apr 5;20(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12905-020-00919-5. BMC Womens Health. 2020. PMID: 32248801 Free PMC article.
-
Statin is a reasonable treatment option for patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2012 Jun;120(6):367-75. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1304619. Epub 2012 May 25. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22639397
Cited by
-
The effects of statins on hyperandrogenism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Dec 20;19(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00863-5. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34930305 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of atorvastatin on testosterone levels.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 22;1(1):CD013211. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013211.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33482034 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase SYVN1 Plays an Antiapoptotic Role in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by Regulating Mitochondrial Fission.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 19;2022:3639302. doi: 10.1155/2022/3639302. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36193086 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of TCM on polycystic ovary syndrome and its cellular endocrine mechanism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 16;14:956772. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.956772. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37260441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simvastatin and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate effects against hypoxic pulmonary hypertension are not additive.Physiol Res. 2022 Dec 16;71(6):801-810. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934913. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Physiol Res. 2022. PMID: 36426885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ehrmann DA. Polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1223–36. - PubMed
-
- Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Consensus Workshop Group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Hum Reprod. 2004;19:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Vrbikova J, Hill M, Starka L, et al. The effects of long-term metformin treatment on adrenal and ovarian steroidogenesis in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 2001;144:619–28. - PubMed
-
- Perrini S, Laviola L, Nataticchio A, et al. Associated hormone declines in aging: DHEAS. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005;28(3 Suppl):85–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

